* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2.3- Winds and Ocean Currents
Marine biology wikipedia , lookup
Marine debris wikipedia , lookup
Marine pollution wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
El Niño–Southern Oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Indian Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Meteorology wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem of the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre wikipedia , lookup
Marine habitats wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on oceans wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric convection wikipedia , lookup
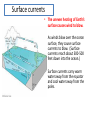
2.3- Winds and Ocean Currents Pages 62-66 Wind • Weather is the condition of the atmosphere at a certain time and pace. • Wind direction and speed are important to forecasting weather. • Global winds circulate heat around the atmosphere. Ocean Currents • An ocean current is a mass of moving water. • As ocean currents move water, they carry heat around the globe. • Currents transfer heat around the planet through convection. Surface currents • The uneven heating of Earth’s surface causes wind to blow. • As winds blow over the ocean surface, they cause surface currents to blow. (Surface currents reach about 300-500 feet down into the ocean.) • Surface currents carry warm water away from the equator and cool water away from the poles. Weather and Climate • The ocean, air, and sun work together to create weather. • Climate describes the weather conditions in a place over a long time. • Scientist use amount of precipitation and temperature when they classify climates. Review Questions- answer these questions IN COMPLETE SENTENCES in the summary/reflection part of your notes. 1. How does heat circulate around the earth? 2. What is weather? 3. What causes wind to blow?