* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bacteriophage - Mrs. Yu`s Science Classes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
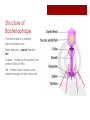
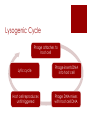
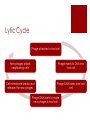
Bacteriophage Yvonne Lin AP Bio 2 a.k.a. Phages Bacterial VIRUS Attacks, infects, and replicates within bacteria Discovered by Frederick Twort (Great Britain, 1915) Species specific – named after the group or species it infects Structure of Bacteriophage Can be simple or complex Size and shape vary Basic features – capsid (head) + tail Capsid – made up of proteins that protect DNA or RNA Tail – hollow tube, nucleic acid passes through to infect host cell Lysogenic Cycle Phage attaches to host cell Lytic cycle Host cell reproduces until triggered Phage inserts DNA into host cell Phage DNA mixes with host cell DNA Lytic Cycle Phage attaches to host cell New phages attack neighboring cells Phage inserts its DNA into host cell Cell membrane breaks and releases the new phages Phage DNA takes over host cell Phage DNA starts to make new phages in host cell Applications Phage therapy – treat bacterial infections that are resistant to antibiotics by destroying them Phage typing – identify pathogenic bacteria Kill specific bacteria found in food (eg. Cheese) Lambda phage Enterobacteria phage λ (coliphage λ) Infects bacteria Escherichia coli (E. coli) Most studied in genetic researches Used as a vector for the cloning of recombinant DNA Thank you for listening Sources: http://textbookofbacteriology.net/phage.html http://phages.org/bacteriophage/ http://www.cellsalive.com/phage.htm