* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AncientRomePowerPoint
Berber kings of Roman-era Tunisia wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Augustus wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Rome (TV series) wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
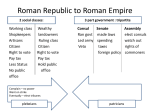
Rome (Geography) Italy Rome Tiber River Rubicon River Po River Alps Mountains Sicily Sardinia Carthage Danube River Rhine River Gaul Britannia Hispania Greece Asia Minor Egypt Israel Rome (Geography) Rome (Geography) Rome Romulus and Remus Twin brothers who founded Rome. (Mythical account) Vestil Virgin and the God Mars She-wolf and farmer Tension between brothers Early Rome Rome was dominated for centuries by their northern neighbors the Etruscans. Rome gained much of their traditions and culture from the Etruscans. Romans belonged to a group of people called Latins. Rome is located in an area called Latium. Rome (Social Classes) Powerful nobles who owned land and had a lot of wealth were called Patricians (Roman Aristocracy). All other free citizens were called Plebeians. You were born into your social class. Rome (Family Life) Patriarchal Society Father (paterfamilias) was head of the household and held responsibility for everything that happened within the family. A woman’s place was in the home to teach the children values. Traditional Roman Values Discipline Self-sacrifice Devotion to family and republic High morals The Republic Rome breaks free of Etruscan monarchs and declare themselves a Republic in 509 B.C. Patricians are the ones who establish the Republic. Plebeians are originally excluded. The Republic Establishment of the Roman Senate Consuls Elected representatives of the people. Veto power Dictator Twelve Tables are the establishment of written law. The Republic Table IV. Paternal Power. 1. – A notably deformed child shall be killed immediately. 2a. – To a father . . . shall be given over a son the power of life and death. 2b. – If a father thrice surrenders a son for sale the son shall be free from the father. 3. – To repudiate his wife her husband shall order her . . . to have her own property for herself, shall take the keys, shall expel her. 4. – A child born within ten months of the father's death shall enter into the inheritance . . . Rome 391 B.C. Roman Expansion by 264 B.C. Roman Expansion by 129 B.C. Roman Expansion by 44 B.C. Roman Expansion by A.D. 14 Roman Expansion by A.D. 117 Roman Army In 391 B.C. Rome is sacked by invading peoples from the north called Gauls. This disaster led to reforms in the military that would help Rome to overcome all other enemies hereafter Roman Army Army organized into groups of 5000 to 6000 men called Legions. Within each Legion men were assigned to groups of 100 (centuries) led by a centurion. Each individual soldier is called a Legionnaire. Roman Army The Citizen soldier - Every Roman male was required to make or purchase his own weapons and armor. - It was expected of every male citizen to answer the call to arms when the country goes to war. Roman Expansion (Italy) Rome comes to dominate the Italian peninsula through two sets of wars Samnite Wars Romans adapt and learn from their setbacks and defeats. Pyrrhic Wars King Pyrrhus of Epirus “Pyrrhic Victory” Roman Expansion (Punic Wars) Carthage Phoenician settlement located in North Africa (present day Tunisia). Empire built off of trade. 1st Punic War Carthage and Rome come into conflict over the Greek city of Massena on the island of Sicily. Rome’s powerful army versus the Carthaginian Navy. 1st Punic War War lasts 23 years. But Rome wins most of the battles. Rome builds a fleet and defeats the Carthaginians in their own element. Carthage surrenders and agrees to pay indemnities. 1st Punic War Outcomes of the 1st Punic War 1. 2. 3. Rome begins it’s overseas empire by taking Sicily and Sardinia from Carthage. Rome is now considered a major Mediterranean power. Rome now has a well trained and large navy. 2nd Punic War Carthage strikes back against the Roman Republic in 221 B.C. led by a general named Hannibal. 2nd Punic War Hannibal creates a power base for Carthage in Spain He leads an army from Spain, across the Alps Mountains , into Italy. 2nd Punic War Although outnumbered Hannibal gains major victories over the Roman armies in Italy. Battle of Ticinus Battle of Lake Trasimine Battle of Cannae Hannibal reached the walls of Rome at one point just to retreat because his army got sick. “Hannibal knew how to gain a victory, but not what to do with it.” 2nd Punic War While Hannibal is wreaking havoc in Italy. A Roman general by the name of Scipio is winning victories over Carthage in Spain. 2nd Punic War Battle of Zama Scipio and Hannibal face off against each other at a place not too far from Carthage called Zama. Scipio defeats the seemingly unbeatable Hannibal. 2nd Punic War After Zama Hannibal is forced into hiding. Carthage has to give up all of it’s overseas possessions to Rome. 3rd Punic War In 146 B.C. Rome goes to war once again with Carthage. This time no peace treaty. The city of Carthage is completely destroyed and salted. Rome 391 B.C. Roman Expansion by 264 B.C. Roman Expansion by 129 B.C. Roman Expansion by 44 B.C. Roman Expansion by A.D. 14 Roman Expansion by A.D. 117 Problems in the Republic Social and Economic Problems of Rome around the year 140 B.C. Rich buy farms from poor farmers Rich use slaves instead of hired workers to farm their lands. Many farmers are called to serve in the army and are not able to up keep their farms. Returning Soldiers, landless poor farmers, and unemployed workers all move to Rome and become part of an ever growing group of urban poor. Tiberius and Gaius Gracchus Two patrician brothers, Tiberius and Gaius Gracchus try to fix the problem of all the landless poor in the city. They propose land reforms to give land back to the people from territories recently conquered in wars with Carthage, Greece, and Spain. These reforms are very unpopular with the Senate, mainly because the Senate is mostly rich landowners. Tiberius and Gaius Gracchus Although loved by the people, the Gracchus brothers were hated by many Senators. Both Tiberius and Gaius are murdered. Marius Reform Gaius Marius comes up with an alternate solution for Rome’s social problems. He removes the law that says you have to own land to be part of the army. As a result, tens of thousands of landless poor join the army. Short term effect: social tensions end. Economy thrives. Long term effect: The Roman Army is no longer based off of loyalty to the Republic. Only to the commanding general. Social War Soon after the Marius Reforms the subjugated peoples of Italy decide to rebel against Rome. They didn’t rebel because they wanted to break off from Rome, they rebelled because they wanted to be considered full citizens of Rome. After years of fighting the Italians get what they want, full citizenship. Sulla Sulla, a patrician general, helps end the bloody social war only to start a civil war against Marius. After winning the civil war he proclaims himself dictator. He basically gets rid of anyone who disagrees with him. Once he felt Rome was ok again he voluntarily retired. Rome: Republic to Empire 1st Triumvirate Julius Caesar Pompey Conquered Gaul Conquered Syria and Palestine Crassus Defeated Spartacus slave rebellion Rome: Republic to Empire Rome: Republic to Empire Crassus is killed in Mesopotamia. Caesar defeats Pompey and makes himself Dictator for Life. Senate becomes afraid of his power and murders him. Rome: Republic to Empire Marc Antony, one of Caesar’s generals joins with Octavian (Caesar’s nephew) to punish Caesar’s murderers. After they defeat Caesar's murderers they turn on each other. Octavian defeats Marc Antony and Cleopatra in the Battle of Asculum which finally brought an end to this period of civil war. Roman Empire Octavian becomes Imperator of Rome (Dictator for Life) and is renamed Augustus Rome is now an Empire not a Republic (Although the Senate is still around). Pax Romana (The Roman Peace) lasts almost 200 years Pax Romana and the 5 Good Emperors Rome is first ruled by 2 dynasties Julio-Cluadians Flavians Both are beset with intrigue, rebellions, assasinations, and madness. The years (96 – 180 A.D.) saw the reign of what is now called the 5 good emperors Nerva Trajan Hadrian Antoninus Pious Marcus Aurelius Christianity and Rome During the time of the emperors Augustus and his son Tiberius (1 – 33 A.D.) a new religion appears within the Empire called Christianity. Christianity begins with a man named Jesus Christ who lived and ministered in the province of Palestine. Within a few hundred years this religion came to dominate the Mediterranean World. Christianity and Rome For over 200 years Christians are persecuted within the Roman Empire until Emperor Constantine makes Christianity the official religion of the empire. Constantine also moves the capital from Rome to Byzantium and renames the city Constantinople. Fall of Rome Empire splits into two halves by Emperor Diocletian in the year 284 A.D. Western Roman Empire (Rome) Eastern Roman Empire (Constantinople) Fall of Rome Fall of Rome Barbarian Invasions Huns Visigoths (Attila the Hun) These guys are ancestors of the Vikings Vandals Ostrogoths Fall of Rome Reasons for Decline of Rome Do not hold to traditional values 1. No longer adapt to new circumstances Corrupt officials and emperors 2. 3. 4. No more loyalty to country Become overwhelmingly greedy Causes social unrest and economic crisis Barbarian invasions