* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 6 Lesson 2 Ocean Currents
Southern Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Diving in the Maldives wikipedia , lookup
El Niño–Southern Oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Marine debris wikipedia , lookup
Marine biology wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Indian Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Marine pollution wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem of the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on oceans wikipedia , lookup
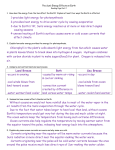
Unit 6 Lesson 2 Ocean Currents What are ocean currents? • ________ ________ are stream like movements of water in the ocean. • __________ _______ are ocean currents that occur at or near the surface of the ocean, caused by wind. • The ______ _______ is one of the strongest surface currents on Earth. What affects surface currents? • Surface currents are affected by continental ________, the _________effect, and __________ winds. • When surface currents meet __________, they are deflected and change ____________. • The deflection of moving objects from a straight path due to Earth’s rotation is called the ________ __________ • In the ________ Hemisphere, currents are deflected to the right. • In the _________Hemisphere, currents are deflected to the left. • _______ _______ can push ocean water across Earth’s surface to create surface currents. 1 Unit 6 Lesson 2 Ocean Currents What powers surface currents? • The major source of energy that powers surface currents is the ________. • The sun heats air near the _________ more than it heats air at other _________. As a result, there are differences in pressure in the __________. • Winds form as a result of __________in air pressure and create _________ currents. How do deep currents form? • _______ _________ are movements of ocean water far below the surface. They are caused by differences in water density. • ________ is the amount of matter in a given space or volume. • _________ and ___________ cause differing ocean water densities. • ____________ is a measure of the amount of dissolved salts or solids in a liquid. Higher _________ makes water more dense. • _______ water is denser than ______ water. 2 Unit 6 Lesson 2 Ocean Currents • Dense water _____ and can form deep water currents that flow along the ocean floor or on another layer of denser water. What are convection currents? • ________ ________ in the ocean are the movement of water that results from density differences. • Convection currents can be ________, _______, or _________. How do convection currents transfer energy? • Water at the ocean’s surface _________ energy from the sun, and surface currents carry this energy to _______ regions. • As warm water reaches a colder region, it cools, becomes denser, and _______. • As _____ surface water moves away, ______ water rises to the surface. The cold water absorbs the sun’s energy, and the cycle continues. What is upwelling? • __________ is the process by which winds blow warm water away from a shore, allowing cool, nutrient-rich water to rise to the surface. • Upwelling supplies the ________ that support the growth of ____________ and _________________. 3 Unit 6 Lesson 2 Ocean Currents • These tiny organisms are food for larger organisms, such as _______ and _________. • Ocean currents can _________ various living organisms to different parts of the world. • Turtles, coconuts, and phytoplankton all ride the ocean’s _______ __________. What do ocean currents transport? • Convection currents in the ocean transport energy in the form of ______. • Ocean currents can release energy into the ___________, making currents an important influence on climate. • Ocean water also ________ dissolved solids, including nutrients, and dissolved gases that support the growth of many marine organisms 4