* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download crusades
Rhineland massacres wikipedia , lookup
Northern Crusades wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Nicopolis wikipedia , lookup
Savoyard crusade wikipedia , lookup
Fourth Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Albigensian Crusade wikipedia , lookup
First Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Despenser's Crusade wikipedia , lookup
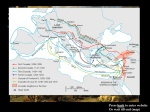
Unit 1 Introduction to World Civilizations and New Ideas Sub Unit 3 The Middle Ages Lesson 12 The Christian CRUSADE The Christian CRUSADE C – Centralization of Government For years Germanic tribes fought wars in Western Europe but by 1050 AD Western Europe had settled down and farming and trade began to expand This time period is called the “late Middle Ages”, during this time the Church began doing things the Roman Empire used to do such as collecting taxes and establishing courts The Christian CRUSADE R – Religious Influence Many Christians left the world behind as monks and nuns who lived in monasteries and convents Many rejected the luxuries of life to take care of the sick and homeless, others learned to farm and taught the local community Many welcomed travelers and supplied teachers to new towns The Christian CRUSADE U – Uniform Translations Monks and nuns were among the few who were literate, could read and write, so they copied books from the past Monasteries soon became centers for learning and kept the knowledge about the past alive (history) Books were copied by hand because machines were not invented The Christian CRUSADE S – Some Christians visited the Holy Land During the Middle Ages, Christians called Palestine the Holy Land and traveled there to visit holy cites where Jesus ministered In the 800’s AD, Islamic leaders conquered Palestine and limited Christian travel to the Holy Land Eventually they grew violent and Christians were not welcomed The Christian CRUSADE A – A Call for a Crusade Pope Urban II was the head of the Roman Catholic Church He called for a Crusade (holy war) against Islamic control The pope promised salvation to those who died on the crusade For a period of 200 years Asia and Europe were at war The Christian CRUSADE D – Determined to Fight Most crusaders believed they were following God’s orders, others wanted adventure, some wanted to escape the hard work at home Kings and nobles joined to gain more power and influence The pope offered forgiveness of sins and The Christian CRUSADE E – European Changes The Crusades opened up trade routes in Europe and Asia Europeans now had access to new and past cultures Trade routes created economic prosperity which increased the desire for travel and exploration