* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BODY DEFENSES AND DISEASE
Vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
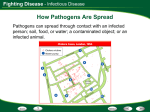
BODY DEFENSES AND DISEASE The 5th Guy CAUSES OF DISEASE Noninfectious Disease When you have a disease, your normal body functions are disrupted. Noninfectious disease ARE NOT spread from person to person CAUSES: Smoking Lack of physical activity High-fat diet CAUSES OF DISEASE Infectious Disease Infectious disease CAN be passed from one living thing to another. CAUSED BY: Pathogens: virus, microorganism or other organisms that cause disease. The 5th Guy 2 PATHWAYS TO PATHOGENS AIR: Some pathogens travel through the air *Example: a single sneeze CONTAMINATED OBJECTS: If you share objects with an infected person, you can become SICK! *Example: contaminated doorknobs, keyboards, combs, and towels PERSON TO PERSON: Some pathogen are spread by direct person *Example: kissing, shaking hands or PATHWAYS TO PATHOGENS ANIMALS: Some pathogens are carried by animals Example: humans can get a fungus called ringworm from handling an infected dog. FOOD AND WATER: Drinking water in the United States is generally safe. But water lines can break allowing germs to enter. Bacteria growing in foods and beverages can cause illnesses Example: meat, fish, and eggs that are not cooked enough PUTTING PATHOGENS IN THEIR PLACE PASTEURIZATION During the mid-1800s, Louis Pasteur discovered that microorganism cause wine to spoil. Pasteur devised a method of using heat to kill most of the bacteria in wine and milk. VACCINES AND IMMUNITY In the late 1700s, no one knew what a pathogen was. Edward Jenner studied a disease called smallpox. He observed that people who had been infected with cowpox seemed to have protection against smallpox. PUTTING PATHOGENS IN The 5th Guy - Flu THEIR PLACE ANTIBIOTICS Have you ever had strep throat? An antibiotic is a substance that can kill bacteria or slow the growth of bacteria Viruses, such as those that cause colds, are not affected by antibiotics. Antibiotics can kill only living things. A virus is NOT a living thing. Vaccines A substance prepared from killed or weakened pathogens. How could a vaccine prevent the spread of disease? Stimulates the body to produce immunity. How is being vaccinted similar to being infected with a disease? Used to trigger the body to make memory cells for a specific pathogen How is it different? YOUR BODY’S DEFENSES FIRST LINE OF DEFENSE For a pathogen to harm you, it must attack a part of your body. YOUR BODY’S FIRST LINE OF DEFENSE IS YOUR SKIN! Your skin is made of many layers of fat cells. The outermost layers are dead. As a result, many pathogens that land on your skin have difficulty finding a live cell to infect YOUR BODY’S DEFENSES FAILURE OF THE FIRST LINES OF DEFENSE Sometimes, skin is cut or punctured and pathogens can enter the body. THE BODY ACTS QUICKLY! Blood flows to the injured area Cell parts in the blood called platelets, which help seals the wound. The increased blood flow also brings cells that belong to the IMMUNE SYSTEM. CELLS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM The immune system consists mainly of three kinds of cells. MACROPHAGE BIG EATERS Engulf and digest microorganisms or viruses. If only a few microorganism or viruses have entered a wound, the macrophages can easily STOP THEM. It alerts the rest of the immune system of invaders CELLS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Lymphocytes - T cells and B cells On the surface of each lymphatic cell are receptors that enable them to recognize foreign substances. These receptors are very specialized - each can match only one specific antigen. Helper T Cell Helper T cells are the major driving force and the main regulators of the immune defense. Their primary task is to activate B cells and killer T cells. The killer T cell is specialized in attacking cells of the body infected by viruses and sometimes also by bacteria. It can also attack cancer cells. CELLS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM B Cells The B lymphocyte cell searches for antigen matching its receptors. If it finds such antigen it connects to it, and inside the B cell a triggering signal is set off. The plasma cell is specialized in producing specific protein, called an antibody, that will respond to the same antigen that matched the B cell receptor. Antibodies are released from the plasma cell so that they can seek out intruders and help destroy them. Challenges to the Immune System Allergies – over reaction to foreign antigens that are not dangerous to most people. (ex. Peanuts, penicillin, mold, etc.) Cancer – a group of diseases in which cells divide at an uncontrolled rate. (ex. Skin cancer) Immune Deficiency – HIV/AIDs; specifically infects the T-cells. Auto-immune Diseases – cells mistake body cells for foreign antigens; ex rheumatoid arthritis What is the differenece between an allergy and an autoimmune disease? In an autoimmune disease, the immune system attacks the body’s own cells. In an allergy, the immune system reacts to foreign cells that are for the most part harmless; such as pollen, foods or medicine.