* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Neuromuscular junctions
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
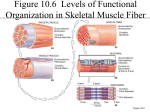
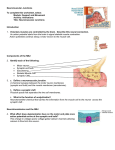
Neuromuscular Junction (NMJ) Neuromuscular junction • Neuromuscular junction : the synapse between motor neuron and muscle fibre • Motor neurons : are the nerves that innervate (power) muscle fibres • Motor unit : single motor neuron and the muscle fibre it innervates • Axon: nerve fibre that is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron 2 • As an axon approaches muscle, it divides into many terminal branches • Each of these axon terminal forms special junction a neuromuscular junction with one or more muscle fibre 3 5 Synaptic Terminal • Contains molecules of Acetylcholine (ACh) • ACh is a neurotransmitter chemical released by neurons to change the membrane properties of other cells. Synaptic Cleft • A narrow space that separates the synaptic terminal of the neuron from the sarcolemma surface. • Contains Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) which breaks down Ach Motor End Plate • The surface of the sarcolemma that contains membrane receptors that bind ACh Nerve Stimulus to Muscles • Neuromuscular junctions – association site of nerve and muscle Nerve Stimulus to Muscles • Synaptic cleft – gap between nerve and muscle – Nerve and muscle do not make contact – Area between nerve and muscle is filled with fluid Sequence of events 1. An action potential arrives at the end of a motor neurone, at the neuromuscular junction. 2. This causes the release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Sequence of events 3. This initiates an action potential in the muscle cell membrane (Sarcolemma). 4. This action potential is carried quickly into the large muscle cell by invaginations in the cell membrane called T-tubules. Sequence of events 5. The action potential causes the sarcoplasmic reticulum to release its store of calcium into the myofibrils. 6. Ca2+ causes tropomoysin to be displaced uncovering myosin binding sites on actin. 7. Myosin cross bridges can now attach and the cross bridge cycle can take place. 8. Relaxation is the reverse of these steps Neuromuscular junction: Note Ach = Acetylcholine In Summary… Sequence Of Events At Neuromuscular Junction Action potential Ca2+ Presynaptic terminal Voltage-gated Ca2+ channel Action potentials arrives at the presynaptic terminal causes voltage-gated Ca2+ channels to open. 29 Sequence Of Events At Neuromuscular Junction Ca2+ Synaptic vesicle Acetylcholine Ca2+ diffuse the cellcauses and cause synaptic to release Ca2+ uptake into the into terminal release of vesicles the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter molecule. acetylcholine into synaptic cleft, which has been synthesized & stored into synaptic vesicles 30 Sequence Of Events At Neuromuscular Junction Ca2+ Presynaptic terminal Synaptic cleft Acetylcholine • Ach travels across the synaptic cleft to postsynaptic membrane which is alsodiffuses known as motor end plate. terminal across the 31 Acetylcholine from the presynaptic