* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Muscle Contraction
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
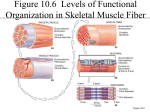
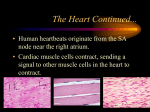
Chapter 6 Muscle Contraction Yesterday... Titin − largest known protein with 26,926 amino acids − C132983 H211861 N36149 O40883 S693 Muscle Contraction skeletal muscle is voluntary or involuntary? so we need a stimulus to begin the process of contraction What else do you need for a contraction to occur? Thick and thin filaments need to interact Need to transfer the message from the neuron to the muscle cell What ions play a role? Is ATP important? Contraction begins at neuromuscular junction Neuron skeletal muscle requires stimulus (nerve impulse) to contract motor unit = one neuron + muscle cells it stimulates neuron − axon − axon terminal synaptic cleft What happens at neuromuscular junction? What happens at the neuromuscular junction? nerve impulse causes acetylcholine (ACh) release from axon terminal − diffuses across synaptic cleft − attaches to receptors Neuromuscular junction What happens at neuromuscular junction? sarcolemma becomes temporarily more permeable to Na+ and K+ Na+ enters cell, K+ leaves change in electrical conditions creates an action potential What is an action potential? electrical current − travels entire sarcolemma once started, is unstoppable results in muscle cell contraction Action potential results in contraction…how? remember that myosin (thick) and actin (thin) slide along each other to shorten sarcomere what triggers the sliding? − release of Ca2+ from SR Look at the sarcomere when Ca is released… 2+ Cross bridges form between filaments What is the role of ATP? myosin is like a mousetrap Botulism what is it? how does it work? − blocks ACh release Botox