* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Punnett Squares
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Human–animal hybrid wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Human leukocyte antigen wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
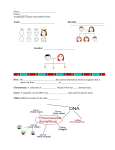
PUNNETT SQUARE VOCABULARY 1 Punnett Squares were invented by Reginald Punnett to help predict the genetic outcomes of crosses between parents carrying specific traits. 2 A Punnett Square is made up of four smaller squares. Each square is worth 25%. T = tall (dominant) t= short (recessive) 3 The different forms of the same trait or gene are called alleles. For example, the gene that controls height in pea plants has one allele for tall height and one for short height. 4 An offspring inherits two alleles for each trait. An offspring may inherit two alleles for the same form of a trait or two different alleles. 5 When two alleles are present, the form of the dominant allele appears. A dominant allele is the one that occurs most often. It is represented with a capital letter. It only takes one gene for it to show up. 6 The allele that is hidden when a dominant allele is present is called the recessive allele. The form of the trait determined by It occurs least often. The recessive allele appears only when two recessive alleles are inherited. 7 Dominant and recessive alleles can be used to explain Mendel’s observations. An organism that has two identical (same) alleles for a trait is called a purebred. Miss Ellie, from Tennessee, was voted the ugliest purebred in the U.S.8 Another name for purebred is homozygous. The prefix homo means same. A purebred has the same alleles, either two dominant (TT) or two recessive (tt). This horse is a purebred Arabian stallion. 9 An organism that has two different alleles for a trait is called a hybrid. In a hybrid, the dominant allele appears, so all the F1 generation plants were tall. These hybrid Labradoodle puppies had purebred Poodle and Labrador Retriever parents. 10 Another name for hybrid is heterozygous. The prefix hetero means different. A hybrid has two different alleles (Tt), but the dominant trait is the one that shows. 11 (?)Some interesting hybrids (?) 12 13 When plants from the F1 generation produced offspring, some of the plants received two dominant alleles, some received one dominant and one recessive allele, and some received two recessive alleles. 14 The plants that received two recessive alleles were short. All others were tall. 15 The genotype is the code for the trait like BB or bb. Remember: genotype = genes 16 The phenotype is the physical characteristic that is expressed like blue eyes or brown eyes. Remember: phenotype = physical 17 18 In the above example, the alleles for the father are written across the top of the square (TT). 19 The alleles for the mother are down the side (tt). 20 T T t Tt Tt t Tt Tt This Punnett Square shows purebred dominant (TT) and purebred recessive (tt) parents. 21 T t T t TT Tt Tt tt This Punnett Square shows parents that are both hybrids. They have one dominant allele (T) 22 and one recessive (t). Punnett squares can be used to calculate the probability or likelihood that a certain combination will occur among the offspring. The higher the probability, the more likely it is to happen. 23 In the above Punnett square, the probability that the flower will be purple is 3 out of 4 or ¾ which is .75 or 75%. 24 Look again at the chart for plant height. What is the probability that the offspring will be tall? 25 Test Practice 1. Genes are carried by structures called _________. A. chromosomes B. alleles C. hybrids D. dominants 26 2. A scientist crossed a tall pea plant with a short pea plant. Out of the offspring, 42 plants were tall and 14 were short. What percentage were short? A. 10% B. 13% C. 25% D. 50% 27 3. A scientist crossed a purebred long-winged fruit fly with a purebred short-winged fly. Long wings are dominant over short wings. What is the probability that the offspring will have long wings? A) 25% B) 50% C) 75% D) 100% 28 Fill in your own Punnett square to find out the percentage of long-winged flies. 29 4. In humans, the allele for a cleft chin (C) is dominant. A woman with the genotype cc has children with a man with the genotype Cc. If the couple has six children, how many do you think would have a cleft chin? A) 0 B) 1 C) 3 D) 6 30 Fill in your own Punnett square to find out how many children will have a cleft chin. 31