* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Punic Wars - Johnson Graphic Design
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Structural history of the Roman military wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the mid-Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Roman infantry tactics wikipedia , lookup
Berber kings of Roman-era Tunisia wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republican governors of Gaul wikipedia , lookup
Rome (TV series) wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
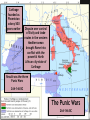
Carthage v. Rome
264 – 146 BC
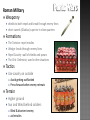
Roman Military
All citizens required to serve
Roman citizens usually made good soldiers
valued loyalty, courage, respect for authority.
Courage in the field = Loyalty to Rome
2
keys to Military success
Organization & fighting skill
ordered troops fight more effectively
most troops rushed wildly at the enemy, relying on
numbers, better soldiers, or luck
Can’t always rely on these factors, Romans turned to
strategy.
Each situation was handled differently, taking into
account terrain, strengths of enemy, strengths of
Roman troops.
The Roman Legion- military unit of 5,000 infantry (foot
soldiers) supported by cavalry (horseback)
Roman Military
Weaponry
shields to both repel and break through enemy lines
short swords (Gladius) superior in close quarters
Formations
The Tortoise- repel missiles
Wedge- break through enemy lines
Repel Cavalry- wall of shields and spears
The Orb- Defensive, used in dire situations
Tactics
Use cavalry on outside
Avoid getting outflanked
Press forward when enemy retreats
Terrain
Higher ground
Sun and Wind behind soldiers
Blind & disorient enemy
aid missiles
If
a unit fled during battle 1 out of 10
soldiers in the legion were put to death.
Roman Decimation
10 soldiers draw lots, loser is killed by other 9
Remaining 9 forced to eat barley and camp
outside of fortifications for a few days
Roman Expansion
Treatment
of Conquered:
forge alliances
offer citizenship
granted privileges
keep customs, money, and local governments
had to pay taxes
loyal to Rome
supplied Roman army with troops.
Roman soldiers stationed throughout the land
Roads built to link territories to Rome.
Latin emerges as the spoken language
By
265 BC Rome controls Italian peninsula
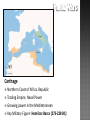
Carthage
founded as
Phoenician
colony 500
years earlier
Dispute over control
of Sicily and trade
routes in the western
Mediterranean
brought Rome into
conflict with the
powerful North
African city-state of
Carthage
Result was the three
Punic Wars
264-146 BC
The Punic Wars
264-146 BC
Carthage
Northern Coast of Africa, Republic
Trading Empire, Naval Power
Growing power in the Mediterranean
Key Military Figure: Hamilcar Barca (275-228 BC)
Sicily
Partially controlled by Carthage
Independent Greek City-State of Syracuse
Rome enters conflict to stop Carthaginian growth
Syracuse becomes Roman ally
Carthage sends land force to face Romans
First Punic War (Land power v.s. Sea power)
Primarily Naval Battle
Carthage Large Navy, experienced
Quinquereme- 5 sets of rower (300), 420 total crew
Romans reverse-engineered them from scrap
Routinely beat smaller, inexperienced Roman Navy
Tactics-
Out maneuver, ram, and sink enemy ships
Bay of Salimas, Greeks v. Persians
Corvus
Roman ships would pull up beside enemy ships
Drop bridge with spike & soldiers board and attack
Some debate if this actually existed
Romans made tactical adjustment- fought to strength
Naval battles turned into mini-land battles
Outcomes
Both sides win battles
Rome keeps rebuilding forces, spending money
Carthage Loses
sues for peace
loses control of various Islands, including Sicily
returns all POWs, had to pay for theirs
Naval dominance gone
Rome Wins
First major expansion beyond Peninsula
Demonstrated their ability to beat main rival
Improved Naval force
Second Punic War- Hannibalic War
Hannibal Barca 247-181/83 BC
Son of Hamilcar
leading commander in First Punic War
Hannibal groomed to lead Military
took oath to always fight Rome
Raised in Spain, left Carthage at age 9
Father killed/ dies in battle
Eventually assumes control of army
Compared to Alexander the Great, Julius
Caesar, & Scipio Africanus as greatest
military generals of all time
Second Punic War- Hannibalic War
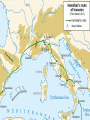
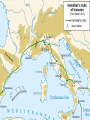
Hannibal attempts to provoke
Rome in Saguntum (Spain)
Crosses the Rhone River
Plans to enter Rome from North
through the Alps to catch them off
guard.
faces Terrain, Weather, Tribes
roughly 16 days to cross
46 000 soldiers enter, 26 000
survive, but battled tested
37 War Elephants, few survived
Hannibal moves into Po River Valley, North Italy
Battle of Trebia
1st major battle in Italy
Roman forces routed, mass casualties
Provoke Romans, Draw them across Trebia River
Force Roman cavalry
from the field
Spring ambush with
hidden force sweeping
behind them
Encircle and slaughter
Gauls hate Rome,
switch sides
Second Punic War- Hannibalic War
Battle of Cannae
Battle of Cannae
Hannibal defeating Romans throughout Peninsula
Fabian Strategy- Rome avoids direct battle
Not Popular, many felt it was delaying the real battle
Return to more aggressive approach
Hannibal wants to cut off supply to city
Rome calls largest force ever assembled- 100 000
Rome Legions are
encircled & slaughtered
50-70 000 dead
Entire family lines lost
City of Rome terrified
Allies switching sides
Battle of Cannae
City of Rome waiting for attack, weakened
Hannibal decides against siege
Forces improved by defection
doesn’t think he has the numbers (3 to 1)
Hannibal wants to make a deal, sends envoy to Rome
Rome fears peace terms would show weakness
Rome says NO- Victory or Destruction
Despite Victories, Hannibal is not accomplishing goals
Unable to break Rome, gain allies & territories
Carthage Government unwilling to send reinforcements
Hannibal is left isolated in Italy
Scipio Africanus 236-183 BC
Son of Roman General
Considered great Military commander
Survived Cannae
Named General in mid-20’s
Roman forces rebuilt
All allies want to fight back
Offer citizenship to slaves, non-citizens
that join military, boys trained
Scipio takes the fight to Carthage- Spain & North Africa
Wins multiple battles, Carthage to sue for peace
Instead recall Hannibal from Italy
Oath to protect Carthage/ defeat Rome- he comes home
Second Punic War- Hannibalic War
Battle of Zama
Hannibal returns, Carthage preps for War
Hannibal’s forces spent, not what they use to be
Reinforcements from home, including 80 War Elephants
Planned to have elephant charge break Legions, then
attack with cavalry and infantry
Scipio formed soldiers into columns, uses trumpets to
disoriented elephants
Elephants either stampede own forces or move down
“isles” between soldiers- damage own Cavalry
Romans spread out to match length of Hannibal’s forces
Bloody battle, no real winner until…
Roman cavalry return to field and encircle foe
Called “Roman Cannae”
Outcome
Hannibal survives, convinces Carthage to ask for peace
Government agrees
Rome takes control of Spain and North Africa
Hannibal continues to fight, supports whoever rallies
against Rome
Constantly on the run
Mercenary/ Military mind for hire
Rome wants to capture their greatest enemy.
"Hannibal ante portas" ("Hannibal is at the gates!")
Home in Spain gone, Carthage Government willing to turn
him over
Roman forces closing in, Hannibal poisons himself to avoid
humiliation/capture
Carthage finished after Second Punic War
economy shattered
lost all territory to Rome
Romans feared revival
used break in treaty to attack Carthage
Rome wins easily
Carthage population sold into slavery- 50 000
City burned
site sown with salt so that nothing would ever grow there
again
Carthage completely disappeared
Not
normal approach for defeated enemies
Why?
Rome now the dominant power in Mediterranean