* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download first nine weeks review ppt 2015
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
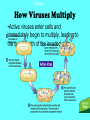
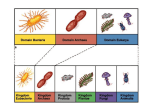
9 Weeks Test Review Aristotle--- was the first to place living things into categories according to where they lived and if they had “blood” LINNAEUS • Linnaeus--- the “Father of Taxonomy” He came up with the two word naming system called binomial nomenclature BINOMIAL NOMENCLATURE • Binomial nomenclature---the two word naming system (Genus species) TAXONOMY • Taxonomy – the science of how living things are classified YOU • What is your scientific name? Homo sapiens • What does it consist of? Genus and species • How to write it correctly?Homo sapiens LEVELS • List the major levels of classification from highest/broadest to lowest/most specific • Domain-KingdomPhylum-ClassOrder-FamilyGenus-Species • Dumb king phillip chased old fat girl scouts DOMAINS • 3 Domains and characteristics of each • 1Archaea – unicellular organisms that can live in harsh conditions; Prokaryotes • 2Bacteria – unicellular organisms that are also Prokaryotes • 3Eukarya – unicellular and multicellular Eukryotes ANIMALS • Characteristics of the animal kingdom – Animals are multicellular – many cells, heterotrophic (eat food), eukaryotes (have a nucleus) HYPOTHESIS • Hypothesis – a possible explanation for a set of observations or answer to a scientific question • Will more chocolate chips make cookies taste better? Experiments • Controlled experiment - An experiment in which only one variable is manipulated at a time Controlled Variable • . Controlled Variable – the variables that are not changed in an experiment Operational Variable • Operational Variable – how to measure a variable or define a term. Manipulated or Independent Variable • 3. Manipulated Variable – the only variable that is changed in an experiment – ex – chocolate chips! Responding Variable • Responding Variable – the factor that may change as a result of the manipulated variable EX - TASTE CLASSIFYING • Classifying – placing into groups based on criteria Observing • Observation – using your senses Types of Observations • Quantitative vs. qualitative observations – numbers vs no numbers Homeostasis • Allows organisms to maintain stable conditions! • THE ODDS & ENDS KINGDOM Cilia---Hairlike structures Used for movement/locomotion by some bacteria and protists Contractile vacuoles (some are star shaped) PARAMECIUM Pseudopods • Pseudo pods---false feet • Used for movement/locomotion by Amoebas Flagella • Flagellum--- long whip like structures • Used for movement by Euglena Flagellum! DNA • What is found in nucleus of cell? DNA – the genetic material • Where is genetic material of a bacteria cell found? Loose in the cytoplasm Virus • 5. Draw and label the structure of a virus - Viruses How Viruses Multiply •Active viruses enter cells and immediately begin to multiply, leading to the quick death of the invaded cells. Virus • How are viruses like parasites?they harm the host • Viruses can REPRODUCE like living things, but are not alive! Bacteria Shapes • Shapes of Bacteria--spirilla (spiral), Cocci (spherical), and Bacilli (rodshaped) Sexual Reproduction • Draw and explain conjugation Sexual reproduction in which genetic material is exchanged between 2 parents. The offspring is more genetically different than those produced by binary fission Asexual Reproduction • Binary Fission Asexual reproduction in which a cell splits and the offspring is identical to the parent Eukaryotic cells • Animal Cells are which type? Eukaryotic cells • What is their outer covering?cell membrane PRODUCER • Producer – An organism that is at the base of the food chain that makes their own food. THE PRODUCERS HAVE THE MOST ENERGY IN THE FOOD PYRAMID AND WEB! Consumers • Consumer – An organism that cannot make their own food and must eat producers or other consumers Definitions • Prokaryotes – no true nucleus • Eukaryotes – have a nucleus • Autotrophs – make their food (producers) • Heterotrophs – eat food (consumers Biology • Biology – The study of living things CELLS • Unicellular – one cell • Multicellular – many cells