* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 6 kingdoms
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
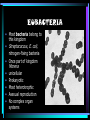
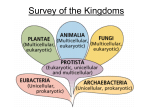
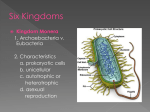
What kind of organisms are these? 6 KINGDOMS EUBACTERIA • Most bacteria belong to this kingdom • Streptococcus, E. coli, nitrogen-fixing bacteria • Once part of kingdom Monera • • • • • unicellular Prokaryotic Most heterotrophic Asexual reproduction No complex organ systems Why are Bacteria important? • • • • Nitrogen fixation Decomposition Help aid in digestion Flavor cheese, sour cream, yogurt • chemosynthesis HOWEVER: Some bacteria cause disease (pathogenic) ARCHAEBACTERIA Means “ancient bacteria” Thought to be some of oldest living things Live in harsh environments such as hot acidic springs or deep in the ocean near hot vents Carry out chemosynthesis (most autotrophic) Used to be part of kingdom Monera Unicellular, prokaryotic, asexual reproduction PROTISTA Protozoa: “first animal” Eukaryotic Unicellular Fresh & salt water habitats & moist soil Some parasitic Heterotrophic Sexual & asexual reproduction Most motile • No complex organ systems AUTOTROPHIC PROTISTS • Seaweeds, diatoms, dinoflagellates, algae • Make their own food • Some unicellular, some multicellular • Some systems place them in PLANT kingdom • But no true leaves, roots, stems, seeds FUNGI Mushrooms, molds, mildews Most multicellular Eukaryotic Nonmotile Heterotrophic Cell walls Reproduce by spores HYPHAE filaments that secrete enymes for digesting food (mycelium: intertwined hyphae) Why are Fungi important? Decomposition Edible/food Antibiotics However: Some carry diseases (ringworm, athlete’s foot) Some destroy crops (rusts & smuts) PLANTAE • Grasses, weeds, flowers, shrubs, trees • Multicellular • eukaryotic • Autotrophic/ photosynthesis • Nonmotile • Sexual & asexual reproduction ANIMALIA • Sponges, jellyfish, worms, squid, clams, insects, crabs, starfish, fish, frogs, reptiles, birds, mammals • Multicellular • Eukaryotic • Heterotrophic • Motile • Sexual reproduction A Classification Dilemma • This organism is an Euglena… • It’s unicellular…mobile…eats other organisms…contains chlorophyll…makes its own food • Where does it belong?? PROTISTA And what about Viruses?? Are they alive?? LIVING CHARACTERISTICS • Organized: head, tail, nucleic acid • Contain DNA or RNA • contain a PROTEIN coat • Adapt (protein coat for protection; can mutate) • Viruses can reproduce (make more of itself…BUT… NON LIVING CHARACTERISTICS • Need HOST organism to make more viral parts & function at all • Replicate rather than reproduce • Don’t grow • Don’t develop • Don’t respond (antibiotics nor other drugs don’t work on viruses STRUCTURE OF VIRUSES BACTERIAL VIRUSES ANIMAL VIRUSES PLANT VIRUSES VIRAL DISEASES ANIMAL PLANT • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Influenza (flu) Common cold Mumps measles Chicken pox Herpes HIV Tobacco mosaic Alfalfa mosaic Lettuce mosaic Potato X Tomato bushy stunt Citrus psoriasis Grapevine fanleaf Viral Infection LYTIC VIRUS • enter host cell…begin making parts immediately (flu or mumps virus) LYSOGENIC VIRUS • Enter host cell; but remains inactive for period of time (HIV, herpes viruses) VACCINE….weakened form of the virus …injected into a Person to stimulate an immune response WANTED POSTER • You will be assigned an organism • You need to find a picture (mug shot) • You need to include the following information on the poster: • Price (on its head) • Kingdom it belongs to • Phylum it belongs to (*you may also need to know the class) • 3 characteristics • Location (where does it live?) • How does it feed?