* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download first nine weeks review ppt 2015
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
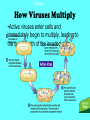
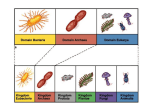
9 Weeks Test Review Aristotle--- was the first to place living things into categories according to where they lived and if they had “blood” LINNAEUS • Linnaeus--- the “Father of Taxonomy” He came up with the two word naming system called binomial nomenclature BINOMIAL NOMENCLATURE • Binomial nomenclature---the two word naming system (Genus species) TAXONOMY • Taxonomy – the science of how living things are classified YOU • What is your scientific name? Homo sapiens • What does it consist of? Genus and species • How to write it correctly?Homo sapiens LEVELS • List the major levels of classification from highest/broadest to lowest/most specific • Domain-KingdomPhylum-ClassOrder-FamilyGenus-Species • Dumb king phillip chased old fat girl scouts DOMAINS • 3 Domains and characteristics of each • 1Archaea – unicellular organisms that can live in harsh conditions; Prokaryotes • 2Bacteria – unicellular organisms that are also Prokaryotes • 3Eukarya – unicellular and multicellular Eukryotes ANIMALS • Characteristics of the animal kingdom – Animals are multicellular – many cells, heterotrophic (eat food), eukaryotes (have a nucleus) HYPOTHESIS • Hypothesis – a possible explanation for a set of observations or answer to a scientific question • Will more chocolate chips make cookies taste better? Experiments • Controlled experiment - An experiment in which only one variable is manipulated at a time Controlled Variable • . Controlled Variable – the variables that are not changed in an experiment Operational Variable • Operational Variable – how to measure a variable or define a term. Manipulated or Independent Variable • 3. Manipulated Variable – the only variable that is changed in an experiment – ex – chocolate chips! Responding Variable • Responding Variable – the factor that may change as a result of the manipulated variable EX - TASTE CLASSIFYING • Classifying – placing into groups based on criteria Observing • Observation – using your senses Types of Observations • Quantitative vs. qualitative observations – numbers vs no numbers Homeostasis • Allows organisms to maintain stable conditions! • THE ODDS & ENDS KINGDOM Cilia---Hairlike structures Used for movement/locomotion by some bacteria and protists Contractile vacuoles (some are star shaped) PARAMECIUM Pseudopods • Pseudo pods---false feet • Used for movement/locomotion by Amoebas Flagella • Flagellum--- long whip like structures • Used for movement by Euglena Flagellum! DNA • What is found in nucleus of cell? DNA – the genetic material • Where is genetic material of a bacteria cell found? Loose in the cytoplasm Virus • 5. Draw and label the structure of a virus - Viruses How Viruses Multiply •Active viruses enter cells and immediately begin to multiply, leading to the quick death of the invaded cells. Virus • How are viruses like parasites?they harm the host • Viruses can REPRODUCE like living things, but are not alive! Bacteria Shapes • Shapes of Bacteria--spirilla (spiral), Cocci (spherical), and Bacilli (rodshaped) Sexual Reproduction • Draw and explain conjugation Sexual reproduction in which genetic material is exchanged between 2 parents. The offspring is more genetically different than those produced by binary fission Asexual Reproduction • Binary Fission Asexual reproduction in which a cell splits and the offspring is identical to the parent Eukaryotic cells • Animal Cells are which type? Eukaryotic cells • What is their outer covering?cell membrane PRODUCER • Producer – An organism that is at the base of the food chain that makes their own food. THE PRODUCERS HAVE THE MOST ENERGY IN THE FOOD PYRAMID AND WEB! Consumers • Consumer – An organism that cannot make their own food and must eat producers or other consumers Definitions • Prokaryotes – no true nucleus • Eukaryotes – have a nucleus • Autotrophs – make their food (producers) • Heterotrophs – eat food (consumers Biology • Biology – The study of living things CELLS • Unicellular – one cell • Multicellular – many cells