* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
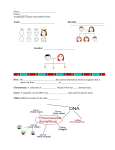
What is heredity? Heredity - the passing on of characteristics (traits) from parents to offspring. Genetics is the study of heredity. • Gregor Mendel Modern genetics is based on Mendel’s explanations for the patterns of heredity in garden pea plants. • Gregor Mendel – a monk in the 1800s who studied pea plants and their traits. Study of Heredity Characters- physical features that are inherited. Traits – several possible forms of a character. Gametes – haploid male or female cell Mendel crossed the peas Fertilization - the uniting of male and female gametes. Cross - combining gametes from parents with different traits. What Did Mendel Find? He discovered different laws and rules that explain factors affecting heredity. Explaining mendel’s results The Mendelian theory of heredity forms the foundation of modern genetics. Mendelian theory explains simple patterns of inheritance. Different traits result from different versions of genes. Mendel’s Results Each organism has two alleles for each trait Alleles - different forms of the same gene Rule of Dominance The trait that is observed in the offspring is the dominant trait (UPPERCASE) The trait that disappears in the offspring is the recessive trait (lowercase) Dominant = strong Recessive = weak, “recedes” Law of Independent Assortment The genes for different traits are inherited independently of each other. Equal chance to get an allele Questions... What do we call the trait that is observed? What case (upper or lower) is it written in? What about the one that disappears? What case is it written in? Phenotype & Genotype Phenotype - the way an organism PHYSICALLY looks red hair or brown hair Genotype - the gene combination of an organism AA or Aa or aa Heterozygous & Homozygous Heterozygous - if the two alleles for a trait are different (Aa) Homozygous - if the two alleles for a trait are the same (AA or aa) Dihybrid vs Monohybrid Monohybrid Cross crossing parents with only one trait (AA with aa) Dihybrid Cross - crossing parents with two traits (AAEE with aaee) Questions... What is the phenotype? What is the genotype? What is homozygous? What is heterozygous? What is monohybrid crossing? Using Punnett Squares A Punnett square is a model that predicts likely outcomes of a genetic cross. A Punnett square shows all of the genotypes that could result from a cross. The simplest Punnett square consists of a square divided into four boxes. The letter combination in each box represents one possible genotype in the offspring. Codominance In codominance, neither allele is recessive and the phenotypes of both alleles are expressed. Dihybrid Cross Inheritance of 2 different traits. FOIL! Using Probability A Punnett square shows the possible outcomes of a cross, but it can also be used to calculate the probability of each outcome. Probability - the likelihood that a specific event will occur. Probability can be calculated and expressed in many ways 1:2:1 or 25% 50% 75% Using a pedigree A pedigree is a diagram that shows how a trait is inherited over several generations of a family. Pedigrees can be used to help a family understand genetic disorders. A genetic disorder is a disease or disorder that can be inherited. A pedigree can help answer questions about three aspects of inheritance: sex linkage, dominance, and heterozygosity. Using a pedigree (cont.) A sex-linked gene is located on either an X or a Y chromosome. Traits that are not expressed equally in both sexes are commonly sex-linked traits. Colorblindness is an example of a sexlinked trait that is expressed more in males than in females. Hemophilia