* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
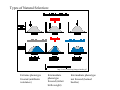
Download Causes of Microevolution
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup