* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download B3Revision LVW
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
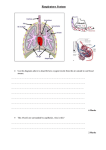
B3 Science Revision •Liver and muscle cells have large numbers of mitochondria •Ribosomes are in the cytoplasm and where protein synthesis happen. •Four different bases, A,T,G,C. •Proteins are made from lots of amino acids joined together. Each amino acid is coded by the sequence (order) of three bases. For example, GGT. •The genetic code needed to make a particular protein is carried from the DNA to the ribosomes by a molecule called mRNA. •mRNA from DNA is called transcription •Proteins from mRNA is called translation Enzymes • Proteins and made from long chains of amino acids • Functions include structural (collagen), • hormones (insulin), carrier molecules (haemaglobin) & enzymes. Enzymes are biological catalysts which catalyse chemical reactions Enzymes use a lock and key mechanism and will denature which change the the shape of the active site at high PH and high temperatures Gene mutations may lead to the production of different proteins, these mutations can happens spotaneously, by radiation or chemicals Respiration • • • • • • • • • • • • Aerobic Respiration Energy is needed for : Glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water Protein synthesis C6H12O6 + 6O2→ 6CO2 + 6H2O Muscle contraction Control of body temperature in mammals ATP Respiratory quotient (RQ) ATP is a substance that is used as the energy RQ = carbon dioxide produced ÷ oxygen used source processes rate in cells. ATP is produced Usually RQ =for 1. manyMetabolic as a result of respiration. For example, one glucose Themetabolic rate is the rate at which energy Anearobic respiration During exercise, the muscle cells respire more than they do at acid rest. molecule can release enough energy during Glucose → lactic is used by the body. Since aerobic respiration This means: respiration for of theoxygen production of: needs oxygen, theberate Oxygen and glucose must delivered to themconsumption more quickly 38used ATP as molecules by aerobic respiration Waste carbon dioxide must be removed quickly can be an estimate ofmore metabolic rate. 2 ATP by anaerobic AchievedThe by increasing the breathing rate and respiration heart rate. ratemolecules of respiration is influenced by changes in temperature and pH. This is because enzymes are involved in respiration, and their activity varies with temperature and pH. • Watson and crick best known for discovering DNA however: • Rosalind franklin and maurice wilkins used xray crystallograhy to take pictures of the DNA. The pictures showed DNA as two chains wound in a double helix • Erwin chargaff discovered there are equal numbers of A and T bases and of G and C bases in DNA Questions • What is a section of chromosome called? • Explain why muscle cells have lots of mitochondria? • Finish the sentence the order of bases in DNA is called the base …….. • Why is collagen needed in the artery walls? • What other name is used to describe enzymes? • Pepsin is an enzyme found in the stomach. It breaks down proteins into amino acids. Draw a diagram to explain why pepsin cannot break down starch. • Higher tier need page 13 in the text book Unicellular vs multicellular An ameoba, a simple unicellular organism Organisms can consist of one cell to many cells: •Simple organisms may be unicellular(consist of one cell) •Complex organisms aremulticellular(consist of many cells) There are advantages to being multicellular rather than unicellular. These include allowing: •The organism to be larger •Cell differentiation (having different types of cells with Mitosis different functions) in •The organisms•Chromosomes to be more complex ‘unzipping’ to form nucleus are copied •Chromatids pulled apart •Cromosoomes separate •Cell divides single strands New double strands forming by complementary base pairing B3 Science Revision Meiosis Produces gametes which are haploid (contain one chromosomes from each pair). Gametes combine to form a diploid zygote Genes on the chromosomes combine to control the characteristics of the zygote. Structure of the sperm ‘unzipping’ to form single strands Acrosome New double strands forming by complementary base pairing Mitochondria Nucleus Tail B3 Science Revision Red blood cells have a large surface area to volume ratio, lack a nucleus and contain haemoglobin. Pulmonary Vena Cava •Haemoglobin + oxygen vein oxyhaemoglobin Right atrium Left atrium •Arteries transport blood away from the heart, Valve • they have thick muscular and Valve elastic walls Right ventricle Left ventricle •Veins transport blood to the heart, they have a large lumen and contain valves Red blood cells: carry oxygen •Capillaries exchanging White blood cells: fight disease materials with Platelets: clot the blood •tissues and are therefore permeable Pulmonary artery Aorta Plasma: the liquid that everything travels in the blood 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. what are the three reasons why the body needs to make new cells? Give an advantage of being multicellular Explain how the sperm is adapted for its job Name the 3 parts of the blood and the job that it does Why is plasma a liquid? What is one way a red blood cell is adapted to its job? Explain why the left ventricle has a thicker muscle wall than the right ventricle? Bacteria cell lack a true nucleus, mitochondria and chloroplasts instead they contain a single circular strand of chromosome Stem cells Undifferrentiate dcells that can develop into different cells. Two types: embyonic (obtained from embryos) and Adult (obtained from a human) Plant growth Animal growth Grows continuously Finite size Restricted to meristems Everywhere Gain height by cell enlargement Cells can differentiate Gain height by Cell division Lose ability to differentiate Genetic engineering • Selection of desired characteristics • Isolation of genes resposible Selective • Insertion of other genes into breeding other programmes These are the steps in selective breeding: • Replication of organismas Decide which characteristics are important Choose parents that show these characteristics http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/science/add_ocr_gateway/living_growing/new Select the best offspring from parents to breed genesrev4.shtml the next generation Repeat the process continuously B3 Science Revision Examples: Genes from carrots and putting them into rice, producing insulin and becoming resistant to herbicides, frost damage or disease to crops. Selective breeding may lead to inbreeding due to a reduction in the gene pool Gene therapy: changing a persons genes in an attempt to Tissue culture cure disorders Cloning technique used to produce dolly: Nucleus removed from an egg cell Egg cell nucleus replaced with the nucleus from the udder cell. Egg cell given an electric shock to make it divide Embryo grows into a clone of the sheep from which the udder cell came • plants grown from cuttings or tissue culture are clones. advantage - can be sure of the characteristics of the plant since all plants will be genetically identical • advantage - it is possible to mass produce plants that may be difficult to grow from seed • disadvantage - if plants become susceptible to disease or to change in environmental conditions then all plants will be affected • disadvantage - lack of genetic variation. • Which part of the cell contains cellulose? • Name three structures found in an animal cell and not in a plant cell? • Name one characteristic of strawberry plants that is useful to gardeners? • Complete the sentence: when a scientist takes ______ from one organism and puts them into another it is called _______ _______ • Which organisms are used to make insulin? • Why would cloning pigs be useful? • how do many plants reproduce? • Describe an advantage and a disadvantage of cloning plants?