* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology - Riverside Military Academy
Ecological resilience wikipedia , lookup
Extinction debt wikipedia , lookup
Source–sink dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Maximum sustainable yield wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Ecological succession wikipedia , lookup
Holocene extinction wikipedia , lookup
Operation Wallacea wikipedia , lookup
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biosphere 2 wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Pleistocene Park wikipedia , lookup
Reforestation wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
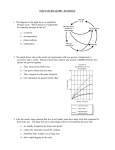
Vocabulary: Define the following terms: Chapter 1: Biology; organism; organization; growth; development; reproduction; species; stimulus; response; homeostasis; adaptation; science; theory; law; peer review; observation; inference; scientific method; hypothesis; experiment; control group; independent variable; dependent variable; constant; data Chapter 2: ecology; biosphere; biotic factor; abiotic factor; population; biological community; ecosystem; biome; habitat; niche; predation; symbiosis; mutualism; commensalism; parasitism; autotroph; heterotroph; herbivore; carnivore; omnivore; detritovore; trophic level; food chain; food web; biomass; matter; nutrient Chapter 3: community; limiting factor; tolerance; ecological succession; primary succession; climax community; secondary succession; weather; climate; latitude; tundra; boreal forest; temperate forest; woodland; grassland; desert; tropical savanna; tropical seasonal forest; tropical rain forest Chapter 4: population density; dispersion; density-independent factor; density-dependent factor; population growth rate; emigration; immigration; carrying capacity; demography; demographic transition; zero population growth; age structure Chapter 5: extinction; biodiversity; genetic diversity; species diversity; ecosystem diversity; background extinction; mass extinction; natural resource; overexploitation; habitat fragmentation; edge effect; biological magnification Critical Thinking: Answer the following question with a claim, evidence, and explanation. Chapter 1: 1. What is the role of energy in living organisms? 2. Compare and contrast a response and an adaptation. 3. Evaluate the statement, “Scientists just perform experiments to prove what they already believe.” Chapter 2: 1. Explain why it is advantageous for organisms such as fungi and algae to form mutualistic relationships. 2. Explain the difference between a habitat and a niche. 3. Describe why food webs are generally better models for explaining energy flow than food chains. 4. Clarify what is meant by the following statement: Grass is just as important as mice in the diet of a carnivore such as a fox. 5. The law of conservation of matter states that matter cannot be created or destroyed. How does this law relate to the cycling of carbon in an ecosystem? Chapter 3: 1. Generalize the difference between a successional stage and a climax community. 2. Infer whether species diversity increases or decreases after a fire on a grassland. Explain your response. 3. Explain why the concepts of limiting factors and tolerance are important in ecology. 4. Describe how successsional stages would differ from primary succesion. 5. In December 2004, a huge iceberg caused a large number of penguin chicks to die of starvation. Ice shelves broke apart in areas where the air temperature increased. The parents of the penguins were cut off from their food source. How is this an example of temperature as a limiting factor? 6. Suggest why biomes are classified according to their plant characteristics rather than according to the animals that inhabit them. 7. Classify a biome that is warm to hot in the summer and cool or cold in the winter and that receives approximately 50-89 centimeters of precipitation annually. Chapter 4: 1. How does the carrying capacity affect k-strategists? 2. Give two examples of how two different density-independent factors can limit a specific population. 3. Explain how competition limits a population’s growth. 4. Predict the shape of a population growth curve for a game park in which a male and female rhinoceros are released. 5. Opossums are solitary animals that usually meet in nature only to mate. What is their probable dispersion pattern? 6. Why might a population continue to grow when the number of births equals deaths? 7. Hypothesize the shape of the age diagram for Switzerland, a developed country in Europe. Chapter 5: 1. Infer why there is more species diversity in southern Florida than there is in northern Alaska. 2. Explain why increased ecosystem diversity contributes to increased biodiversity in the biosphere. 3. Describe three values that the biosphere provides. 4. Describe a service that an ecosystem provides in your community that should be protected to ensure that the quality of the service continues. Graph interpretation 1. Which biome has the greatest number of species? Why? 2. What are the two most fragile biomes? What are the greatest threats to their continuity? 3. Which biome was more prevalent when fossil fuels formed? How did they form fossil fuels? 4. Which biome is characterized by lack of water? Give three examples of organisms that live there that have adapted to water scarcity and explain what their adaptation is. 1. Explain why there are different levels of ice at different times of the season. 2. What is the independent variable? 3. What is the dependent variable? 4. What trend does this graph express? 1. 2. 3. 4. What cause and effect relationship does this graph show? What could happen in the future if this trend continues? What are some possible approaches to avoiding the continuation of this trend? Why is there a connection between a rise in human population and a rise in extinctions? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What does this graph portray? When were the 3 biggest extinctions? What pattern does this map demonstrate? Speculate - what could be the cause of these mass extinctions? What are the conditions under which there are fewer extinctions? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. What does this graph depict? What pattern does it portray? What is the trend? What are the biggest causes of carbon emission? What are the smallest causes of carbon emission? What are the difficulties in decreasing carbon emission? What are the current effects of carbon emission?