* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 7th-cells-and-heredity-unit-1-lesson-2-chemistry-of-life
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
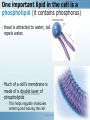
th 7 Science Cells and Heredity (Module A) Unit 1 Lesson 2 Unit 1 Lesson 2 Chemistry of Life THE BASICS! • Element: a substance that cannot be broken down into a simpler substance. • Atom: smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of that element • Molecule: a group of atoms held together by chemical bonds • Some made up of only one type of atom. (N2) • Most made up of two or more types of atoms. (H20) • Compound: substance made up of atoms of two or more different elements (joined by chemical bonds.) • have different properties than the elements that make them. • most molecules found in cells are compounds. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Is it a molecule? Is it a compound? What elements How many are present? atoms are present? O2 – oxygen Yes No O 2 O – oxygen No No O 1 CO2 – carbon dioxide Yes Yes C and O 3 No No He 1 Yes C, H and O 24 No H 1 He – helium C6H12O6 - sugar Yes H - hydrogen No Q: Can something be a molecule without being a compound? A: yes (example?) Q: Can something be a compound without being a molecule? A: no Q: Can something be an atom without being a compound or a molecule? A: yes, but it does not happen in nature veryCopyright often© Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Molecules of Life! • Lipid: is a fat molecule • Mainly used for storing energy • Comes from oils, some fish •Protein: made up of smaller molecules called amino acids. • Used to build and repair body structures • Enzymes (a type of protein) help chemical processes happen in cells. • Found in meat, beans, nuts Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Molecules of Life! • Carbohydrates: include sugars, starches, and fiber. • Used for energy and energy storage • Simple carbohydrates are made of one or a few sugars linked together. Complex carbohydrates contain many sugar molecules linked together • Nucleic acids: molecules that carry information in cells. • Nucleotides- smaller molecules that make up nucleic acids. • DNA is a nucleic acid that carries information that cells need to make other molecules. One important lipid in the cell is a phospholipid (it contains phosphorus) • Head is attracted to water; tail repels water. • Much of a cell’s membrane is made of a double layer of phospholipids • This helps regulate molecules entering and leaving the cell. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 1 Lesson 2 Chemistry of Life Why is water important? • Water moves through a cell membrane by a process called osmosis. • Water moves into and out of a cell, from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration. • Too little water in a cell causes it to shrink. • Too much water in a cell causes it to burst. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company