* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What are atoms and molecules?
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Biomolecular engineering wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Chemical biology wikipedia , lookup
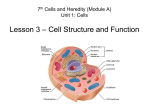
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Carbohydrate wikipedia , lookup
Abiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Unit 1 Lesson 2 Chemistry of Life Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 1 Lesson 2 Chemistry of Life It’s Elementary What are atoms and molecules? • All cells (and all matter) are made up of atoms and molecules. • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down into a simpler substance. • The smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of that element is called an atom. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 1 Lesson 2 Chemistry of Life What are atoms and molecules? • What are the six main elements that make up the human body? Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 1 Lesson 2 Chemistry of Life What are atoms and molecules? • A molecule is a group of atoms held together by chemical bonds. • Some molecules are made up of only one type of atom. • Most molecules are made up of two or more types of atoms. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 1 Lesson 2 Chemistry of Life What are atoms and molecules? • A compound is a substance made up of atoms of two or more elements joined by chemical bonds. • Most molecules found in cells are compounds. • Compounds have different properties than the elements that make them. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company What is a macromolecule? Macro = large There are 4 groups of large molecules that are found in large quantities in our bodies. They are: Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids and Nucleic Acids Macromolecules are polymers. Poly- = many -mer = unit Polymers are long molecules built by linking repeating building blocks or units in a chain A Polymer Here are some analogies to better understand what polymers and monomers are…. EXAMPLE of POLYMER A TRAIN A NECKLACE MONOMER ? ? If the train is the whole polymer, what would be the small groups that make up the train? If the necklace is the polymer, what are the monomers that make up the necklace? Look at the label to the left. 3 of the 4 macromolecules can be found in foods. Organisms use nutrients for energy and as building materials (0 grams in this product) (13 grams in this product) (9 grams in this product) When studying these biochemical molecules, we are interested in finding out….. what they do for living things. what they generally look like. what their monomers are. and how they may help the body gain energy to sustain life. Unit 1 Lesson 2 Chemistry of Life What are some important types of molecules in cells? • A lipid is a fat molecule or a molecule that has similar properties. Lipids have many jobs in cells, such as storing energy. • Your cells get lipids from foods such as olive oil, butter, nuts and fish. • They are made up of chains of triglycerides Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company LIPIDS – What do they do They are a great source of STORED ENERGY so we have it in the future. They INSULATE the body to maintain normal body temperature and they CUSHION the internal organs for protection. They produce hormones for the body called STERIODS They waterproof surfaces of animals,plants, and fruitsthese are waxes! THINK: Waterproof, insulate, steriods, energy, cushion… “WISE C” Unit 1 Lesson 2 Chemistry of Life What are phospholipids? • What causes a cell membrane to have a doublelayer structure? Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 1 Lesson 2 Chemistry of Life What are some important types of molecules in cells? • A protein is a molecule made up of smaller molecules called amino acids. • Protein-rich foods are broken down into amino acids, which make new proteins to build and repair body structures. • Proteins called enzymes help chemical processes happen in cells. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 1 Lesson 2 Chemistry of Life What are some important types of molecules in cells? • Carbohydrates are molecules that include sugars, starches, and fiber. • Cells use carbohydrates for energy and energy storage. • Simple carbohydrates are made of one or a few sugars linked together. Complex carbohydrates contain many sugar molecules linked together. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 1 Lesson 2 Chemistry of Life What are some important types of molecules in cells? • Nucleic acids are molecules that carry information in cells. • Nucleotides are the smaller molecules that make up nucleic acids. • DNA is a nucleic acid that carries information that cells need to make other molecules. • You do not get energy from nucleic acids Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Energy that we gain by the consumption of food is measured in Calories. If you drink a glass of skim milk, you will get a gain of 90 Calories of energy for your body. Energy Gained From Carbohydrates Eating 1 gram of carbohydrate provides your body with 4 Calories. Energy Gained from Lipids Eating 1 gram of fat provides your body with 9 Calories. Notice if you eat 1 gram of fat, you are gaining more than twice the amount of Calories than from a gram of carbohydrate or protein! ENERGY So… MACROMOLECULES Number of Calories it provides Carbohydrates 4 Proteins 4 Lipids 9 Nucleic Acids 0 BIG 4 TEST: Are you smart? If you eat a sandwhich with 46 grams of carbs and 24 grams of protein and 10 grams of fat, how much energy will you gain? Unit 1 Lesson 2 Chemistry of Life Waterworks What are phospholipids? • A lipid that contains phosphorus is called a phospholipid. • The head of a phospholipid molecule is attracted to water. The tail repels water. • Much of a cell’s membrane is made of a doublelayer of phospholipids, which regulates molecules entering and leaving the cell. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 1 Lesson 2 Chemistry of Life Why is water important? • Water moves through a cell membrane by a process called osmosis. • Water moves into and out of a cell, from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration. • Too little water in a cell causes it to shrink. • Too much water in a cell causes it to burst. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company