* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ROME - Spring Branch ISD
Ancient Roman architecture wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
First secessio plebis wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Romanization of Hispania wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Demography of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman technology wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
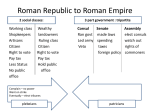
Name:_________________________________ Period:______________ Date:_______ RED Chapter 6 Study Guide Ch. 6, section 1 1. Who were the two legendary founders of Rome? Romulus and Remus 2. What three groups occupied the area that is now Rome beginning in 1000BC? Latins, Greeks, and Etruscans 3. What were the specialties of each group? Etruscans were metalworkers and engineers, Greeks grew grapes and olives, Romans developed religion. 4. Who were the Patricians and Plebeians? (What did they do?) Patricians were aristocratic landowners in power and Plebeians were the common farmers, artisans and merchants who made up most of the population. 5. What is the name of the position that protected Plebeians from unfair Patrician practices? Reporters? Tribunes 6. What two things did the consuls command? Army and government 7. How long were consuls’ terms? One year long 8. How many people belonged to the Senate? What were the functions of the Senate? 300 members 9. How was the Assembly more democratic than the Senate? All citizen-soldiers were members. 10. What was required of all citizens who owned land? To serve in the army. 11. What policy toward defeated enemies helped Rome become a long-lasting empire? Different laws and treatment for different parts of conquered territory. 12. Why did Carthage and Rome fight the Punic Wars? For control of the Mediterranean. RED Chapter 6 Study Guide Page 1 of 4 Name:_________________________________ Period:______________ Date:_______ 13. What did Hannibal do to the Romans in the 2nd Punic War? Inflicted enormous losses on them. 14. sWho finally was able to defeat Hannibal? Scipio 15. How was the 3rd Punic War different than the other two? Carthage was no longer a threat. Ch. 6, section 2 16. What was the most serious problem facing Rome after the Punic Wars? Widening gap between rich and poor. 17. How did Rome acquire so many slaves? Made slaves of the captured peoples. 18. What was the name of the two Tribunes who tried to help Rome’s poor? What happened to them? Tiberius and Gaius Gracchus 19. How did the Roman army of this time differ from the previous Roman army? Generals recruited soldiers from landless poor 20. Who restored order to Rome after Caesar’s death? The Second Triumvirate 21. Why was civil war always a threat when a leader died? No written law for selecting a new emperor 22. What was life like for Roman women? Social equals of men. 23. What was the point of the policy of “Bread and Circuses?” To distract and control the masses. 24. What was the Pax Romania? “Roman Peace”. 24. Give some examples that show Augustus was Rome’s ablest leader. He stabilized the frontier. Glorified Rome with splendid public buildings. Ch 6 Section 3 RED Chapter 6 Study Guide Page 2 of 4 Name:_________________________________ Period:______________ Date:_______ 1. Jesus based many of his teachings on: Monotheism, the Ten Commandments, and other ideas from the Jewish religion. 2. Most of the information about Jesus' life comes from the first four books of the New Testament called the___. Gospels 3. Which of Jesus’ disciples did he refer to as the “rock” on which the Christian Church would be built? Peter 4. As a later convert to Christianity, who wrote letters to the faithful, which became part of the New Testament? Paul 5. In A.D.162, who did the Roman Empire forced into exile in a dispersal called the Diaspora? Jews 6. The first Roman emperor to accept Christianity was Constantine 7. The bishop of was considered the pope, leader of the entire Christian Church. Rome Chapter 6 Section 4. 8. In the third century, the Roman Empire suffered from inflation. What is inflation? Inflation is a large drop in the value of money combined with a rise in prices. 9. What is a reason the Roman army needed to use mercenaries? The discipline and loyalty of Roman troops collapsed 10. What are two things Diocletian did to try to slow the decline of the Empire? Doubled size of army to protect borders & forced farmers to keep farming 11. What was the effect of moving the capital of the Empire to Byzantium? It shifted the power of the empire toward the east. 12. What was the name of the new capital? Rome 13. Who was Alaric? He was the Germanic king who successfully attacked Rome. RED Chapter 6 Study Guide Page 3 of 4 Name:_________________________________ Period:______________ Date:_______ 14. Powerful chieftain of the Huns that terrorized both the empire's Germanic neighbors and the empire itself. Attila Chapter 6 Section 5 1. The people of the Roman town of Pompeii were killed by a volcano. 2. The great Roman epic, the “Aeneid”, was written by Virgil. 3. The accurate histories of Rome, were written by____. Tacitus. 4. The family of languages that developed from Latin are called Romance languages. 5. The design of the Roman aqueducts made significant use of the architectural structure of the arch. 6. The art form called bas-relief is a type of sculpture. 7. All of the following were important principles of Roman law EXCEPT for the idea that all citizens have the right to freedom of religion. RED Chapter 6 Study Guide Page 4 of 4