* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sales Channels - Stevens Institute of Technology
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Customer relationship management wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Customer engagement wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
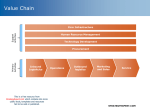
Today’s Topic: Sales & Sales Channels Designing and Managing the Selling, Implementation and Customer Support Process Course Schedule The Marketing Function (Lenovo) Sales & Sales Channels (GolfLogix) Internet-based Marketing (HubSpot) R&D: Product Development (Guidant) Operations (Crocs) Product Launch (Invisalign) Final Exam on Product Launch (Emotiv) Last week: Marketing Learnings Elements of the Marketing Mix (C+4P) Basis of mix decisions: market & financial objectives and competitive advantage Importance of product positioning Positioning factors: - positioning with? (target customers) - positioning against? (relevant competitors) - desires & fears of positioning target - positioning content (differentiators,benefits) Promotion (marcomm): choosing the vehicle(s)/ media that provides best and most cost-effective access to the target Today’s Agenda The basic sales functions Types of sales channels Choosing sales channels GolfLogix--- sales channel selection Readings and assignment for next week (HubSpot) Sales & Sales Channels “Nothing (good) happens until somebody sells something” Sales Channels: Learnings The basic sales functions: (promotion), selling, fulfillment, and service Channel value-added: Higher and lower valueadded channels; value-added functions Specific channel options: direct (multiple types), OEM, integrator, VAR/VAD, distributor, dealer/retailer, etc Channel decision criteria: considerations in matching products, customers, and channels Channel economics: channel margin, profit Channel conflict: coordinating multiple channels Channels are Critical: which channel(s) you use affects… The success you’ll have in selling (revenues) What you have to sell Who you are selling to The price you get for your product The design of the product The functions you’ll have to perform (and associated expenses) in marketing, sales, manufacturing, R&D, IT and finance ---- almost everything! Three Basic Sales Functions Promotion/marketing communications creates the environment for successful sales: making the customer aware and interested Selling: convincing the customer to buy (may sometimes be achieved by promotion alone) Fulfillment: taking the order, delivering the product, installing/configuring/testing Service: delivering post-sale customer support (repair, maintenance, training, consultation/helpline, upgrades, returns, …) Channel Functions: One or more of……….. Information Local advertising Product/brand choices Selling Availability Packaging Logistics Installation/ Configuration Integration Customization Training Maintenance Advice/helpline Warranty/returns Upgrades Repairs Testing Techsonic Which channel(s) for 901? Which channels for GPS? Marine dealers Mass merchants Direct: Techsonic catalog (Direct: internet) Required for sales success…? promotion selling fulfillment service Channel Capabilities function promotion Mass merchants Marine dealers low medium selling very low high fulfillment high very high (marcomm) service low/medium medium/high higher value-add channel “High(er) Value-added” Channels are used for products that are: – Technically complex, and/or… – Higher priced, higher margin (%) – Hard-to-sell/explain (incl. first-of-type); require sales efforts in addition to manufacturer-initiated promotion – Application-specific – Require significant support services (install, configure, maintain, customize, help/advice) ……..and conversely for “low(er) value-added” channels Two Additional Considerations Your channel partner(s) is selling (many) other products, not just yours Channels can (sometimes) accept lower gross margins on products, if they can make money on service, support and add-on sales High-Tech Channel Options Direct (own salesforce, agents, telemarketing, direct mail, catalog, internet) Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) Distributors (“warehouses”) Dealers/Resellers/Retailers VARs/VADs Systems integrators (sell or refer) Consultants (refer) Franchises (uncommon for tech products) Channel Alternatives -- 5 most common in color -- OEM Systs Integr VAR “You” Dealer Distrib Endcustomers Manufacturer-Channel Relationship Elements Price, and volume discounts Contract timeframe Degree of exclusivity Sales area (region or customer type) Product support Selling support Marketing support Delivery commitments (logistical support) … Deciding on Channels - 1 Ability to satisfy customers’ needs Customer decision processes Customer preferences/expectations Market coverage Product characteristics (e.g., complexity) Deciding on Channels -2 Competitive strategy/situation (advantage, shelf space, mind share, preemption, response) Availability of partners Competencies of potential partners Channel management (conflict, cost) Financials (revenue/margin and expense; start-up and ongoing)!! higher value-added channels have higher expenses, and need higher gross margins to make a profit Channel Economics --- example List price = $100 Manufacturer channel price COGS = 35 expenses = 20 65 Channel Partner end user price 90 COGS = 65 expenses = 20 gross margin % = 30/65 = 46% gross margin % = 25/90 = 28% OI % = 10/65 = 15% OI % = 5/90 = 6% Those who sell for you require lots of support…… Training (product and sales) Ongoing technical support Selling support Marketing “air cover” Advertising support (“co-op”) Promotional programs (incl. pricing) Ordering/sales management systems Logistics (delivery/expediting, parts, returns,…) Sales Readings for 11/2 Class Going to Market - read to understand types of sales channels, and the reasons for choosing them GolfLogix: Measuring the Game of Golf (case) GolfLogix Case Summary A start-up company in 2002 Uses GPS technology to aid golfers Two product versions: “distance only” and “complete system” Currently selling to/through golf courses Considering also using retail channels (would require a modification to their product) Sales questions for 11/2 class What are the most significant end-customer and sales channel benefits of the each of the GolfLogix products? What is the market potential (number sold and GolfLogix revenues) of each of the GolfLogix products? Who are the appropriate target customers for the Distance Only product? For the Complete System? What are the positives-and-negatives of selling through golf courses? Through retail channels? If only one of the channels can be chosen, which one should GolfLogix use? Given the option of selling through both channels, should GolfLogix do that? Sales Channels: Learnings The basic sales functions: (promotion), selling, fulfillment, and service Channel value-added: Higher and lower valueadded channels; value-added functions Specific channel options: direct (multiple types), OEM, integrator, VAR/VAD, distributor, dealer/retailer, etc Channel decision criteria: considerations in matching products, customers, and channels Channel economics: channel margin, profit Channel conflict: coordinating multiple channels Reading for Next Week: Internet Marketing HubSpot: Inbound Marketing and Web 2.0 (a case that focuses on “new” methods of promotion using the internet) HubSpot Case Summary Timeframe is 2009 HubSpot was founded in 2006; currently has ~1000 customers Sells “inbound marketing” software that businesses use in their marketing/promotion efforts HubSpot has built its business by (exclusively) using inbound marketing techniques and its own products/tools To grow it’s business further, it faces questions about which customer segment to target, how to generate customer interest/contact, and which of the “interested” customers to pursue… …and whether to engage in outbound marketing Mix elements: Promotion Branding (creating a company or product “image”) Advertising (multiple media; paid and free) Direct marketing (mail, catalog, telemarketing, internet) “Reference” customers (testimonials) Public relations Industry relations (trade orgs, industry analysts,…) Trade shows and events Price promotions … Inbound vs. Outbound Marketing Outbound (traditional) marketing “pushes” information about the company and its products out to customers - mass and targeted advertising - trade shows and events - direct mail, etc Inbound marketing “pulls” customers and tries to get them interested enough to contact the company on their own initiative -search engines - blogs - social media, etc Assignment Questions Which customers should HubSpot target: Owner Ollies or Marketer Marys? Why? (see next chart for things to consider in making a decision) Does HubSpot have the right set of products for your chosen target customers? If not, what changes should they make? What are the positives-and-negatives of HubSpot’s software-as-a-service pricing strategy? What benefits would undertaking some outbound marketing have for HubSpot? What outcomes, if any, could outbound marketing deliver better than inbound marketing? (see second following chart, AIDA, for some hints) Selecting Target Customers: some considerations Segment size and revenue opportunity Customer benefits Customer interest (incl. current relationships) Customer ability-to-pay and leverage Competition/market coverage Sales issues: sale time/complexity, cost, channel and associated profit margin Cost to serve/support Customer loyalty/lock-in Customer lifetime value Strategic value AIDA Marketing Model Attention capture customer’s attention; create awareness of the company and/or product Interest create interest in the product’s features, benefits or value Desire customers want it and/or feel that they need it Action customer takes action; buys the product