* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heart Anatomy and Physiology Presentation
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
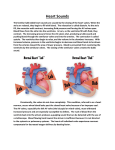
Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System • heart • blood vessels Average Size of Heart • 14 cm long • 9 cm wide 15-2 Location of Heart • posterior to sternum • medial to lungs • anterior to vertebral column • base lies beneath 2nd rib • apex at 5th intercostal space • lies upon diaphragm 15-3 Coverings of Heart 15-4 Wall of Heart Three layers • endocardium • forms protective inner lining • membrane of epithelial and connective tissues • myocardium • cardiac muscle • contracts to pump blood • epicardium • serous membrane • protective covering • contains capillaries and nerve fibers 15-5 Heart Chambers Right Atrium • receives blood from • inferior vena cava • superior vena cava • coronary sinus Right Ventricle • receives blood from right atrium Left Atrium • receives blood from pulmonary veins Left Ventricle • receives blood from left atrium 15-6 Heart Valves Tricuspid Valve • right A-V valve • between right atrium and right ventricle Bicuspid Valve • left A-V valve • between left atrium and left ventricle Pulmonary Valve • semilunar valve • between right ventricle and pulmonary trunk Aortic Valve • semilunar valve • between left ventricle and aorta 15-7 Coronal Sections of Heart 15-8 Heart Valves Tricuspid Valve Pulmonary and Aortic Valve 15-9 Skeleton of Heart • fibrous rings to which the heart valves are attached 15-10 Path of Blood Through the Heart 15-12 Path of Blood Through the Heart 15-11 Blood Supply to Heart 15-13 Cardiac Cycle Atrial Systole/Ventricular Diastole • blood flows passively into ventricles • remaining 30% of blood pushed into ventricles • A-V valves open/semilunar valves close • ventricles relaxed • ventricular pressure increases Ventricular Systole/Atrial diastole • A-V valves close • chordae tendinae prevent cusps of valves from bulging too far into atria • atria relaxed • blood flows into atria • ventricular pressure increases and opens semilunar valves • blood flows into pulmonary trunk and aorta 15-17 Heart Actions Atrial Systole/Ventricular Diastole Atrial Diastole/Ventricular Systole 15-16 Heart Sounds Lubb • first heart sound • occurs during ventricular contraction • A-V valves closing Dupp • second heart sound • occurs after ventricular contraction • semilunar valves closing Murmur – abnormal heart sound 15-18 Heart Sounds 15-19 Cardiac Muscle Fibers Cardiac muscle fibers form functional syncytia • group of cells that function as a unit • atrial syncytium • ventricular syncytium 15-20 Cardiac Conduction System 15-22 Muscle Fibers in Ventricular Walls 15-23 Regulation of Cardiac Cycle • physical exercise • body temperature • concentration of various ions • potassium • calcium 15-28 Pulmonary Circuit • consists of vessels that carry blood from the heart to the lungs and back to the heart 15-50 Blood Flow Through Alveoli • cells of alveolar wall are tightly joined together • the high osmotic pressure of the interstitial fluid draws water out of them 15-51 Systemic Circuit • composed of vessels that lead from the heart to all body parts (except the lungs) and back to the heart • includes the aorta and its branches • includes the system of veins that return blood to the right atrium 15-52