* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download bio 241 – fall 2009 – examination #1
Survey
Document related concepts
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
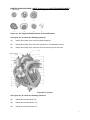
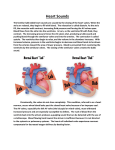
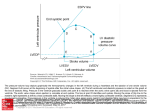
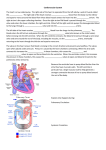
Transcript
BIO 241 EXAMINATION #1 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM BLOOD and HEART READ THESE DIRECTIONS TEST #_______ BEFORE STARTING THE TEST, 1. Write your name and test number at the top of the scantron sheet. 2. Fill in the bubbles for your name (last, first) on the back of the scantron sheet. 3. Write your name on the front of the written answer sheet. TURN IN YOUR SCANTRON SHEET AND WRITTEN ANSWER SHEET. YOU MAY KEEP THE REST OF THE TEST. THE ANSWER KEY WILL BE POSTED ON MY WEBSITE. YOU MUST TURN IN THE TEST 10 MINUTES BEFORE THE HOUR. EXCEPTIONS. THERE WILL BE NO REMEMBER THE ACADEMIC HONOR CODE pledge you took below: “As a student at The University of North Carolina Wilmington, I am committed to honesty and truthfulness in academic inquiry and in the pursuit of knowledge. I pledge to uphold and promote the UNCW Student Academic Honor Code.” _______________________________________________________________________________ Each of the following questions or incomplete statements below is followed by suggested answers or completions. Select the one BEST answer in each case and fill in the appropriate circle on the computer sheet. (2 pts each) 1. Which of the following statements about blood is false? A. Formed elements make up about 45 percent of blood. B. Normal pH of blood is between 7.35 and 7.45. C. Volume of blood in healthy adult males is 5-6 L. D. Most plasma proteins are produced by the spleen. E. None of the above is false. All are true 2. Oxygen is transported by red blood cells by binding to: A. Specific receptors on the plasma membrane of the RBC. B. Specific receptors within the nucleus of the RBC. C. The beta polypeptide chain of the globin portion of the hemoglobin molecule. D. The polypeptide chain of the heme group within the hemoglobin molecule. E. The iron (Fe2+) atom in the heme portion of the hemoglobin molecule. 3. Which Phagocytic Functions of WBCs in the Inflammatory Response involves the white blood cells squeezing through the spaces inbetween the endothelial cells of the capillary wall? i A. margination B. chemotaxis C. diapedesis D. pavementing E. ameboid motion 4. The SECOND most numerous white blood cells are the: A. lymphocytes B. neutrophils C. eosinophils D. monocytes E. basophils 1 5. Place the following events that occur after Red Blood Cell Death in the correct order 1. Bilirubin excreted in feces. 2. Destruction of RBC by phagocytes 3. Iron is stored as ferritin or hemosiderin 4. Proteins broken down into amino acids A. 1-2-3-4 B. 4-2-1-3 C. 2-4-3-1 D. 4-3-2-1 E. 2-3-4-1 6. Which one of the following statements about the platelet phase of hemostasis is TRUE ? A. Platelets secrete factors that promote primary hemostasis. B. Most clotting factors circulate as inactive precursors. C. Platelets can adhere to exposed collagen fibers. D. ADP and thromboxane A2 can cause platelets to aggregate. E. All of the above. 7. The most abundant proteins in blood plasma are A. globulins. B. transport proteins. C. albumins. D. lipoproteins. E. fibrinogens. 8. The conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin is catalyzed by the enzyme A. fibrinogen-converting enzyme. B. plasmin. C. factor VIII. D. thrombin. E. prothrombinase. 9. When a person who lives at sea level vacations in the Rocky Mountains, you would expect A. a drop in oxygen levels. B. the release of erythropoietin. C. a rise in hematocrit. D. both A and C E. A, B, and C 10. In adults, red bone marrow is located in the A. sternum and ribs. B. shaft of long bones. C. iliac crest, body of vertebrae. D. A, B, and C E. A and C only 11. Place the following processes of Hemostasis in order 1. Formation of Fibrin strands 2. Adherence of platelets 3. Cells & Fibrin forms a Clot 4. Release of enzymes 5. Retraction of Clot 6. Vascular spasm A. 1-2-3-4-5-6 B. 6-2-4-1-3-5 C. 2-4-1-3-5-6 D. 5-6-4-3-2-1 E. 1-3-5-6-2-4 2 12. Which of the clotting systems start when tissue thromboplastin appears following damage to vessel wall? A. Intrinsic System B. Platelet System C. Chemotatic System D. Extrinsic System 13. The first common intermediate factor of both the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of blood clotting is __________ which combines with calcium, PF3 and Factor Five to form___________. A. Factor II; prothrombin B. Prothrombin Activator; Thrombin C. Fibrinogen; Fibrin D. Factor X; Prothrombinase E. Plasminogen; Plasmin 14. The leukocyte that spends the little time in the circulating blood, moving quickly into the tissues to become wandering macrophages, is the: A. Neutrophil. D. A and C are correct, but not B. B. Eosinophil. E. A, B, and C are correct. C. Monocyte. 15. During the normal cardiac cycle, the ventricles contract when they are directly stimulated by the: A. Sinoatrial node. D. Baroreceptors of the carotid sinus. B. AV node. E. Vagus nerve. C. Purkinje fibers. 16. Chordae tendineae function to: A. Pull the walls of the ventricles toward each other during contraction, causing the generation of tremendous pressure. B. Open the semilunar valves so that blood can be ejected from the heart. C. Open the AV valves so that there is easy flow of blood from the atria. D. Prevent movement of the AV valve cusps into the atria during ventricular systole. E. Move the AV valves into the ventricles during atrial systole. 17. The normal decrease in speed of conduction from the AV node into the AV bundle (the physiologic heart block) results in: A. Failure of the ventricles to contract in time with the atria. B. Adequate time for the ventricles to fill with blood. C. Delayed opening of the Av valves. D. A decrease in the rate of blood flow from the atria into the ventricles. E. An extra atrial depolarization phase prior to ventricular depolarization. 18. Using the following numbered list of structures, determine the answer that indicates the proper sequence of structures encountered by a drop of blood in the normal vascular supply to the heart muscle itself. 1. Left ventricle 7. Thebesian veins 2. Right ventricle 8. Cardiac veins 3. Aortic semilunar valve 9. Epicardium 4. Mitral valve 10. Myocardium 5. Pulmonary semilunar valve 11. Right atrium 6. Coronary arteries 12. Left atrium A. B. C. 1, 4, 6, 10, 9, 8 11, 2, 3, 10, 6, 8 1, 3, 6, 10, 8, 11 D. E. 2, 5, 6, 10, 8, 12 3, 1, 6, 8, 10, 9, 11 3 19. Which one of the following is true concerning the lub-dup sounds of the heart: A. the first sound is longer and louder and is caused by closure of the tricuspid valve; the second sound is shorter and sharper and is caused by closure of the mitral valve B. the first sound is shorter and sharper and is caused by closure of the tricuspid valve; the second sound is longer and louder and is caused by closure of the mitral valve C. they are caused by contraction of the ventricles, followed by contraction of the atria D. the first sound is longer and louder and is caused by closure of the AV valves; the second sound is shorter and sharper and is caused by closure of the semilunar valves E. the first sound is shorter and sharper and is caused by closure of the semilunar valves; the second sound is longer and louder and is caused by closure of the AV valves 20. If heart rate increased to very high levels, and all other factors remained the same, then: A. the autonomic nervous system will release more epinephrine to the SA node to slow down the heart rate. B. Stroke volume will increase to cardiac output the same as at rest. C. The oxygen content of the blood will fall to levels insufficient to maintain life. D. End-diastolic volume will decrease because ventricular filling time is drastically shortened. E. End-systolic volume will increase because the heart valves are open for only a short time. 21. The right atrium receives blood from the A. coronary sinus. B. superior vena cava. C. inferior vena cava. D. A, B, and C E. B and C only 22. Compared to the right ventricle, the left ventricle has all the following characteristics, except that it A. has a thicker wall. B. is composed of cardiac muscle cells. C. pumps a greater volume. D. works harder. E. produces about six to eight times more pressure when it contracts. 23. The following is a list of vessels and structures that are associated with the heart. 1. right atrium 2. left atrium 3. right ventricle 4. tricuspid valve 5. left ventricle 6. venae cavae 7. aorta 8. pulmonary arteries 9. bicuspid valve 10. pulmonary veins What is the correct order for the flow of blood entering the heart from the pulmonary circulation? A. 8, 2, 4, 5, 7, 6, 1, 9, 3, 8, B. 10, 2, 9, 5, 7, 6, 1, 4, 3, 8 C. 10, 1, 9, 3, 8, 2, 4, 5, 7, 6 D. 6, 2, 9, 5, 8, 10, 1, 4, 3, 7 E. 6, 1, 4, 3, 8, 10, 2, 9, 5, 7 4 24. The foramen ovale in the fetal heart is located in the A. right atrium. B. left atrium. C. right ventricle. D. left ventricle. E. interatrial septum. 25. The circumflex branch and the anterior interventricular artery are branches of the A. right coronary artery. B. left coronary artery. C. interventricular artery. D. coronary sinus. E. aorta. 26. During the cardiac cycle, the A. P wave of the ECG occurs between the first and second heart sounds. B. atrial repolarization coincides with the QRS complex of the ECG. C. second heart sound occurs during atrial systole. D. first heart sound coincides with the QRS complex of the ECG. E. both B and D 27. All of the following are true of the cardiac conduction system EXCEPT A. The AV node can take over the pacemaking task if the SA node is damaged. B. Autonomic nervous system impulses establish the fundamental rhythm of the heart. C. The pacemaking ability of the AV bundle alone is not sufficient to maintain homeostasis. D. Ectopic pacemakers may be stimulated by caffeine or nicotine. E. ACh release by the parasympathetic division of the ANS decreases SA node depolarization. 28. Cardiac output can be increased by all of the following except one. Choose the exception. A. increasing preload B. increasing end systolic volume C. increasing stroke volume D. increasing ejection fraction E. increasing heart rate 29. Which of the following is greater during left ventricular systole? A. the peak pressure in the aorta. B. the peak pressure in the ventricle. C. Neither is greater. 30. Which of the following would be greater? A. the end-diastolic volume when the heart rate is 60 beats/minute B. the end-diastolic volume when the heart rate is 150 beats/minute 31. Abnormally slow depolarization of the ventricles would most change the shape of the ________ ECG tracing. A. P wave B. T wave C. QRS complex D. P-R interval E. R-T interval in an 5 32. The parasympathetic neurons of the cardiovascular center of the medulla decrease cardiac output and release norepinephrine. The sympathetic neurons of the cardiovascular center of the medulla cause an increase in heart rate and force of contraction. A. The first statement is true but the second statement is false. B. The first statement is false but the second statement is true. C. Both statements are true. D. Both statements are false. 33. Which of these would cause stroke volume to increase? A) when venous return is decreased B) when venous return is increased C) when diastolic blood pressure in aorta is decreased D) both A and C E) both B and C 34. A patient has an EDV of 90 mL and an ESV of 40 mL with a heart rate of 50. What is this patient’s cardiac output? A. 6500 mL/min or 6.5 L/min B. 2000 mL/min or 2.0 L/min C. 4500 mL/min or 4.5 L/min D. 2500 mL/min or 2.5 L/min E. 180 mL/min or 0.18 L/min FILL-IN-THE-BLANK. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question on your written answer sheet. (1 pt each) 35) The percent fraction of formed elements relative to whole blood is the _________. 36) Platelets are pinched off from giant multinucleated cells in the bone marrow called ________. 37) White blood cells that are increased in allergic individuals are the _________, 38) The visceral pericardium is the same as the ___________. 39) The inferior point of the heart is called the ________. 40) A positive ________ agent such as epinephrine increases contractility of the heart. 6 IDENTIFICATION QUESTIONS: WRITE Answers on your WRITTEN ANSWER SHEET!!! ( 1 pts each) (assume pink orange granules in #3) Figure 19-1 The Origins and Differentiation of Formed Elements Use Figure 19-1 to answer the following questions: 41) Identify the number of the cell that releases histamine. 42) Identify the number of the cell that is important for cell mediated immunity. 43) Identify the number of the cell that is the most common type of leukocyte. Figure 20-1 The Heart Use Figure 20-1 to answer the following questions: 44) Identify the structure labeled "8." 45) Identify the structure labeled "13." 46) Identify the structure labeled "11." 7 MATCHING- Below are two matching sections. The first matching section covers the cardic cycle. The second matching section covers blood typing. Answers for each section may be used more than once or not at all. Use answer blanks on your written answer sheet. (1 pt each) Matching Section I. A. Isovolumetric Relaxation B. Semilunar Valves C. Ventricular Filling: Passive D. Ventricular Ejection E. Isovolumetric Contraction F. Atrial Systole G. Atrioventricular Valves 47) What valve closes at the very beginning of isovolumetric contraction? G 48) What specific phase begins when the ventricular pressure falls below the aortic pressure? A 49) What phase of ventricular diastole begins at the point when the atrial pressure first becomes greater than the ventricular pressure? C 50) What specific phase begins with opening of the aortic valve? D 51) What specific phase occurs immediately before isovolumetric contraction. F 52) What specific phase begins immediately at the R peak of the QRS complex in the electrocardiogram? E 53) What valve opens at the very end of isovolumetric contraction? B 54) What specific phase begins with the closing of the aortic valve? A Matching Section II A. B. C. D. E. Blood Type A Blood Type B Blood Type AB None ABO group F. G. H. I. J. Blood Type RhBlood Type Rh+ Blood Type O All Rh group 55) The ABO blood type that has no antigens. H 56) The blood type that can receive packed red blood cells from an A, B, and O donor. C 57) The ABO blood type whose plasma contains no agglutinins. C 58) The blood type that contains A agglutinogens. A 59) The blood group that forms antibodies after exposure to the antigen. J 60) The blood type known as the universal donor. H 61) The blood type that can always safely receive A, B, and O plasma. H 62) The blood type of the fetus that can potentially produce a condition known as erythroblastosis fetalis. G 8 WRITTEN ANSWER SHEET Signature Personal Return _____________________ NAME ____________________ TEST NUMBER ________ Fill-in Identification Matching I Matching II 35. _hematocrit/45%__ 41. __4_____________ 47. __G___ 55. _H____ 36. _megakaryocytes________ 42. __6_____________ 48. __A___ 56. _C____ 37. _eosinophils/basophils_____43. __2_____________ 49. __C___ 57. C 38. _epicardium___________ 44. _papillary muscle_ 50. __D____ 58. _A or C__ 39. _apex________________ 45. myocardium_____________51. __F____ 59. _J or F____ 40. _inotropic_______________46. _trabeculae carnae_ 52. __E____ 60. _H____ 53. __B____ 61. _H____ 54. _ A____ 62. _G_____ 63. The graph below has four major regions labeled W, X, Y, and Z. The following questions are in regards to the graph and those regions. Which region of the graph shows an ventricular pressure exceeding aortic pressure?__Y____ Which region of the graph represents ventricular systole and ventricular repolarization? _Y____ Which region of the graph represents atrial diastole, atrial depolarization and atrial contraction? _W Which region of the graph represents end diastolic volume? ____X___________ TOTAL POINTS _____100____ POINTS MISSED ____________ TEST SCORE ___________% 9