* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The_Light_Independent_Reactions
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Chloroplast DNA wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
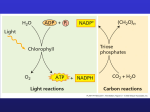
The Light Independent Reactions Objectives • Outline how the products of the light-dependent stage are used in the light-independent stage (Calvin cycle) to produce triose phosphate (TP) – referring also to ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP), ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase (rubisco) and glycerate 3-phosphate (GP). • Explain the role of carbon dioxide in the lightindependent stage. • State that TP (and GP) can be used to make carbohydrates, lipids and amino acids. • State that most TP is recycled to RuBP. The Light Independent Reactions • Occur in the stroma via a cyclic pathway called the Calvin cycle. • They are a result of a sequence of enzyme controlled reactions requiring ATP and reduced NADP (from light dependent stage) and CO2. • CO2 diffuses into the leaf through open stomata, into the air spaces. Describe the path taken by CO2 to get to the chloroplast • Use these key words: Stomata Stroma Spongy mesophyll Air space Palisade mesophyll Thin cell wall Chloroplast envelope Cytoplasm Cell membrane • In the stroma CO2 is fixed by the 5 carbon compound ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) to form an unstable 6 carbon compound. • RuBP is a CO2 acceptor molecule. • This process is catalysed by the enzyme RUBISCO and is a carboxylation reaction • RUBISCO is made in chloroplasts using chloroplast DNA • The 6C compound immediately splits into two molecules of a 3C compound called glycerate-3-phosphate (GP). • ATP and reduced NADP from the light dependent stage are used to reduce glycerate-3-phosphate to produce triose phosphate (TP –a 3 carbon phosphorylated sugar) • One sixth of TP is used to make glucose, amino acids, fatty acids, glycerol or nucleic acids. • Five sixths are used to regenerate more RuBP (this also requires ATP). The Calvin Cycle The Uses of the Calvin Cycle Products • Glycerate-3-phosphate can be used to synthesise fatty acids by entering the glycolytic pathway and being converted to acetyl CoA • TP is used to synthesise glycerol • Glycerate-3-phosphate and inorganic salts are used to synthesise amino acids • Pairs of TP combine to form hexose sugars e.g. glucose • Glucose and fructose combine to form sucrose the main translocatory sugar • Starch is synthesised in the stroma for energy storage • The structural carbohydrate cellulose is also synthesised