* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review 3rd Qtr KEY
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Livermorium wikipedia , lookup
Bent's rule wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Low-energy electron diffraction wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Metastable inner-shell molecular state wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Computational chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Bond valence method wikipedia , lookup
Extended periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Electronegativity wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Metallic bonding wikipedia , lookup
Resonance (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital diagram wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
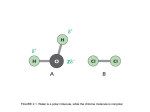
REVIEW: 3rd QUARTER Name: KEY ****MUST SHOW ALL CALCULATIONS*** CHAPTER 1 & 2 : MATTER & MEASUREMENT 1. Complete the following table Chemical or Physical Property Extensive or Intensive Property CHEMICAL = 2 PHYSICAL = 3 EXTENSIVE = 1 INTENSIVE = 4 Melts at 68.0°C Corrosive 2.2 lbs Decomposes in air Magnetic 2. Osmium is the densest element with a density of 22.57 g/cm3. Find the mass of a 56.2 cm3 sample of osmium. 1268 grams 20 mL = ______________cm3 1mL = 1cm3 3. Convert 4. 0.0054 weeks is equivalent to how many minutes? 5. Indicate the # of significant figures then round each to the # of significant figures indicated. 12.5 54.4 minutes has __3__ significant figures & rounded to 2 significant figures is 12 0.0010 has __2__ significant figures & rounded to 3 significant figures is 0.00100 or 1.00 x 10-3 3.5 x 1023 has __2___ significant figures & rounded to 4 significant figures is 3.500 x 1023 6. Given calculations with the calculator answer, write the answers with the appropriate # of significant figures. 13.0 + 46.10 = 59.1 The answer should be 59.1 227 x 0.3 = 68.1 The answer should be 70 CHAPTER 3 & 22 : ATOM & NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY 7. Complete the table for the following isotopes. SYMBOL Atomic # Mass # # of protons # of neutrons # of electrons Zn 20 65 74 34 40 21 18 TOTAL 102 220 102 118 102 8. What one number identifies an element? ___________ 9. How many magnesium sulfate molecules are in 25.0 g? 1.25 x 1023 molecules Mg(SO4) 10. Complete the following nuclear equations a) Decay of polonium-218 by alpha () emission. b) Decay of carbon-14 by beta () emission 11. Carbon-14 has a half-life of 5,730 years. If a plant contained 2.0 g of 14C when it died, how much is left after 34,380 years? mf = 0.03125 mg 12. What is an ISOTOPE? Give examples CHAPTER 4: ELECTRON ARRANGEMENT 13. Explain why chromium’s electron configuration is [Ar] 4s13d5 instead of the expected configuration of [Ar] 4s23d4 Filled & ½ filled orbital’s are more stable. 14. Complete the following question based upon Cobalt (#27) a) Give the noble gas electron configuration for this element: _________________________ b) What are the quantum numbers for this element? _____, _____, _____, _____ c) How many unpaired electrons does this atom have? 3 d) How many outer-shell electrons (valence electrons) does an atom contain? 2 e) How many inner-shell electrons (core electrons) does an atom contain? 25 15. List the quantum numbers for Cadmium (#48): _____, _____, _____, _____ 16. What element is represented by the quantum number 5, 3, 1, +1/2: _________________ 17. Calculate the wavelength if the frequency is 2.5 x 105 Hz. 1200 m 18. Find the energy of a photon if frequency is 7.31 x 1014 Hz. 4.84 x 10-19 J CHAPTER 5 - PERIODICITY 19. Circle the atom with the LARGER radius. a) Ra or N b) Ne or Xe 20. Circle the particle with the LARGER radius. a) Cl or Cl – b) Mg or Mg2+ 21. Circle the atom with the HIGHER first ionization energy. a) Li or Cs b) Ba or As 22. Magnesium reacts with oxygen to produce the ionic solid magnesium oxide (MgO). Which other elements would you predict would react with oxygen in a similar reaction? Explain Elements: Be, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra Alkaline Earth Metals because they all have the same number of valence electrons CHAPTER 7 – NOMENCLATURE & FORMULA WRITING 23. Name the following compounds a) KNO3 ____________________________ b) HBr ____________________________ c) SO3 ______________________________ d) FeCl3 ___________________________ 24. Find the percentage composition of the anhydrate in ZnSO4 • 7H20 56.14 % Anhydrate CHAPTER 6 - MOLECULAR GEOMETRY 25. Ionic bonds are the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged atoms. What determines their strength? Explain 1) Magnitude (Product) of Charge - Increase # Increase bond strength 2) Atomic Radius – Increase size Increase bond strength 26. Which ionic compound has the GREATER ionic bond strength, LiCl or NaCl ? LiCl 27. Which ionic compound has the GREATER ionic bond strength, BaS or K3N ? BaS 28. Ionic compounds generally have (lower or higher) melting and boiling points. 29. Molecular compounds generally have (lower or higher) melting and boiling points. 30. Identify the intermolecular forces involved for each compound below and circle the compound with the stronger intermolecular forces for each pair? For each pair, circle the compound with the strongest IMF INTERmolecular Forces Involved NF3 L.D. D.D. ( EN = 4-3 = 1) N2 L.D. ↑ size ↑ L.D. CH3Cl L.D. D.D. (asymmetrical) NF3 or PF3 N2 or O2 CH3Cl or H2O PF3 L.D. D.D. ( EN = 4-2.1 = 1.9) O2 L.D. H2O L.D. D.D. (asymmetrical) Hydrogen Bonding 31. Why do atoms form chemical bonds? to lower their potential energy & to become stable 32. For each of the following molecules, draw the Lewis electron dot diagram, give the shape, and state whether the molecule is polar or nonpolar. Lewis Diagram Molecular Shape Molecular Polarity SiO2 Linear Nonpolar AsF5 Trigonal Bipyramidal Nonpolar 33. Determine if the following molecules are polar or nonpolar. TeCl2 bent BCl3 Cl Te Cl Cl nonpolar CH2Cl2 C polar Cl NONPOLAR tetrahedral Cl B Cl POLAR trigonal planar H POLAR Cl H nonpolar