* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Quiz
Thin-slicing wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Adherence management coaching wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Social cognitive theory wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
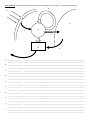
Name:_______________ Date:_______________ Quiz Learning & Memory Define: define the words below to the best of your ability. (3 pts) Psychology: Vocabulary: Choose the term from the list below that best matches each of the following statements. (1 pts each) A. B. Amnesia Conditioned Stimulus C. D. Encoding Memory E. F. Modeling Negative Reinforcement G. H. Punishment Rehearsal I. J. Shaping Unconditioned stimulus _____ 1. Rewarding successively closer approximations of a desired behavior. _____ 2. The process by which information is encoded, stored and retrieved. _____ 3. A reinforcer that decreases the likelihood that a behavior will be repeated. _____ 4. Severe memory loss caused by brain injury, shock, fatigue, illness or even repression. _____ 5. A stimulus that produces an innate response. Main Idea Review: Four choices are given for each statement or question below. Select the best answer. (1 pt per question) 1. _____ Which of the following is the most accurate definition of learning? a. The result of a variety of experiences that temporarily shape behavior. b. An enduring change in an organism’s behavior based on experience. c. The sole result of classical and operant conditioning. d. The association of experiences due to their occurrence in close proximity. 2. _____ After having been struck by a car, a dog now exhibits fear responses every time a car approaches. The dog also exhibits a fear response to the approach of a bus, a truck, a bicycle, and even a child’s wagon. The dog has undergone a process of: a. Stimulus discrimination b. Stimulus generalization c. Spontaneous recovery d. Positive reinforcement 3. _____ Through reinforcement, pigeons are taught to peck at paintings by a Monet artist. The fact that pigeons do not peck at the paintings of DaVinci, Picasso, or Grandma Moses represents: a. Modeling b. Reflexive response c. Stimulus generalization d. Stimulus discrimination 4. _____ Every time you buy ice cream from the Yellow Brick Road ice cream parlor, you get your over-the-rainbow card stamped. Once you purchase ten items, you get your next item free. The Yellow Brick Road ice cream parlor has you on which of the following reinforcement schedules? a. Variable-ratio b. Variable-interval c. Fixed-ratio d. Fixed-interval 5. _____ Operant behaviors are different from those in Classical Conditioning, because in classical conditioning the behaviors are: a. Cognitive b. Involuntary c. Reinforced d. Voluntary Vocabulary: Choose the term from the list below that best matches each of the following statements. (1 pts each) A. B. Albert Bandura B.F. Skinner C. D. Edward Thorndike Edward Tolman E. F. Ivan Pavlov John B. Watson G. John Garcia _____ 1. This behaviorist was concerned with the relationship between reinforcement and learning, and commonly used pigeons, rats, and other animals to demonstrate how primary and secondary reinforcers change behavior. _____ 2. Conducted the “Little Albert” experiment with Rosalie Rayner to demonstrate classical conditioning phenomena. _____ 3. Latent learning psychologist who used rats to prove that rats, and thereby humans, can learn without necessarily expressing their knowledge. _____ 4. Psychologist who first studied operant conditioning, and whose “law of effect” stated behavior is more likely to reoccur if reinforced. _____ 5. Russian dietitian who mistakenly discovered classical conditioning while studying the digestion of dogs. _____ 6. Classical conditioning psychologist who subjected animals to food laced radiation to study taste aversions. _____ 7. Observational learning theorist who had children observe authority figures abusing dolls and carrying out various violent actions and later observed children abusing similar dolls and carrying out similar violent actions. Fill in the Blank: Identify and briefly describe six of letters on the diagram of memory below. (1 pt per letter/descriptiong). E A B G D C F I O H J A. ___________________: __________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________________ B. ___________________: __________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________________ C. ___________________: __________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________________ D. ___________________: __________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________________ E. ___________________: __________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________________ F. ___________________: __________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________________ G. ___________________: __________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________________ H. ___________________: __________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________________ I. ___________________: __________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________________ J. ___________________: __________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________________