* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
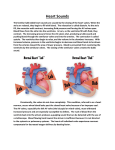
Heart Guided Notes Location Within the ____________________ Pointed ____________ extends to the left. It rests on the ___________________________at the 5th intercostal space. It has a _________________________, lies under the 2nd rib. Pericardium A _________________________________________encloses the heart. Thin ____________________ pericardium= __________________________- hugs the surface of the heart. Loose outer layer= _________________________________________. Pericardial Fluid Slippery _________________________________ produced by the membrane between the ____________________________ layers. It allows the heart to ___________ in a ________________________________________________. Myocardium Heart walls are made of _______________________________________________________. Chambers ____________ hollow chambers that are lined with a ___________ lining called the _____________________________. Atria __________ superior ___________________ chambers that are ____________ walled. Blood flows into and fills the _____________ under __________________________. Ventricles __________ inferior _____________________ (pumping) chambers that are __________ walled. It forces blood ________ of the ____________ and into large _______________. A _______________ divides the heart longitudinally. Includes the ______________________ septum and the _______________________________________ septum. Double Pump _____________________ circulation to ___________ and back. _______________ circulation to _________________________ and back. Pulmonary Circulation: Right side of the ___________ ___________ __________ side of the heart. Systemic Circulation: _________ side of the heart _______________________ __________ side of the heart. Valves ________ valves allow blood to flow _____________________________________. It prevents ______________________. _________ AV valves=________________________________. 2 semilunar valves. AV valves are located between atria and ___________________. It prevents backwash into ___________. __________ AV= _______________ or mitral (2 flaps). __________ AV= ________________ (3 flaps). The AV valves are _______________ to the wall of the ventricles by the ___________________________________. The valves are ___________ when the ventricle is _________________; _______________ when the ventricle is _______________________. Semilunar valves __________ the base of the large arteries _________________ the ventricles. Each valve has _______________ (flaps). When ventricles _________________, they __________; when ________________, they ____________ to prevent _____________________. Pulmonary _______________________-from the __________ ventricle to the ___________________ trunk (artery). Aortic ____________________-from the _________ ventricle to the ____________ artery. Each set of valves open at different times: -__________ opens when _________________ relaxes -________________________ opens when ventricles _________________. Oxygen Poor Blood-pathway through body From the __________ of the body tissue ________________ and ________________ vena cava right ___________ _________________ valve right ____________________ ______________________ semilunar valve Pulmonary ___________ pulmonary __________ branch ____________ and ____________ ___________ picks up ________________ and dumps off __________________________. Oxygen Rich Blood-pathway through body Drained from the lungs ______ pulmonary veins left ___________ ________________ valve left ___________________ ___________ semilunar valve ___________ body tissues dumps off ________________ and picks up carbon dioxide. Cardiac Circulation Although the heart ____________________ are filled with blood almost continuously, that blood does ________ nourish the _______________________. The ___________ and __________ coronary arteries branch from the _________ of the _________ and encircle the heart in a __________________ at the junction of the atria and ____________________. Those arteries are _______________________ when the ventricles __________________ and are only able to supply ______________ to heart muscle between _____________. Rapid heart rate may cause _______________________ blood supply. The _____________ your resting heart rate is, the better _____________________ your heart muscle is. The ______________________ is drained by the coronary _________ coronary ___________ the right ________________. Cardiac Cycle The ___________ and ____________ occurring from one ___________________ to the next. -Systole= _______________________ -Diastole= _______________________ Lub-Dup-Pause “Lub”- ______________ of the _______ valves-longer and __________________-ventricles _______________________ “Dup”- _______________ of ______________________ valves-shorter and __________________ventricles __________________. “Pause” is the heart in complete ______________________ _____________________ are usually problems with the valves ___________________. Atria contract ________________________. As they begin to ______________ ventricles _____________________ (ventricular systole) ventricles _____________ (ventricular diastole). Conduction System ________________ muscle cells can ______________ spontaneously and ____________________. Two types of control systems: -___________________ -___________________ Intrinsic __________________ or Nodal system. A cross between ____________ and _________________ tissue. It has ___________________________ cells and can initiate _______________________________ or trigger _____________________. SA Node -SA= ______________________. Located on the ___________ atrial wall. ______________________starts each beat AV Node _____________________. It’s located on ________________________ septum. Bundle of ________ bundle branches __________________ fibers ventricles ___________________. Extrinsic System Heart contractions cam be changed by _____________________ nerves, __________________, hormones, and ions (________________________________________). ______________ (sympathetic influence) affects _________ node which __________________ heart rate.