* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heart
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
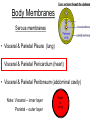
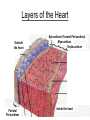
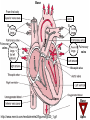
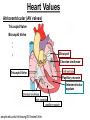
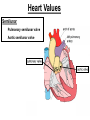
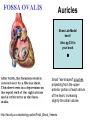
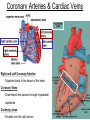
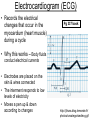
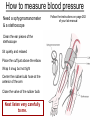
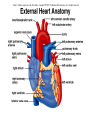
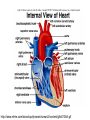
Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab 12: The Heart What you need to Know and Do • Be able to define and identify the terms in you Lab handouts***** – On a model – On a preserved sheep heart – On a diagram • Be able to determine – Systolic and Diastolic blood pressure – pulse pressure – mean arterial blood pressure • What you need to do: Lab 36 & (37, 38) & 39 – Complete parts A and B (lab 36) & label figures – Skip (lab 37 & 38) – Test blood pressure (lab 39) The Heart – Starting from the Outside • Parietal pericardium - outer layer of the pericardium – The pericardium has outer and inner coats • The outer coat is tough and thickened, loosely cloaks the heart. • Epicardium - the inner layer of the pericardium (a.k.a – visceral pericardium) • The inner coat is stuck closely to the heart • Myocardium – Thick middle layer of the heart (contains mostly cardiac muscle) • Endocardium – The inner layer of the heart Body Membranes Serous membranes • Visceral & Parietal Pleura (lung) • Visceral & Parietal Pericardium (heart) • Visceral & Parietal Peritoneum (abdominal cavity) Note: Visceral – inner layer Parietal – outer layer Heart or Lung Layers of the Heart Outside the heart Parietal Pericardium Epicardium (Visceral Pericardium) Myocardium Endocardium Inside the heart Base From the body 9 5 5 4 1 Pulmonary veins 7 6 6 Pulmonary veins 2 Bicuspid valve 3 8 1 Apex http://www.merck.com/media/mmhe2/figures/fg020_1.gif Base Apex Heart Values Atrioventricular (AV valves) Tricuspid Valve Bicuspid Valve Bicuspid Chordae tendineae Tricuspid Valve Papillary muscle Interventricular septum people.eku.edu/ritchisong/301notes5.htm Heart Values Semilunar Pulmonary semilunar valve Aortic semilunar valve Auricles Show Lab Model here!! Also pg 335 in your book Small "ear-shaped" pouches projecting from the upper anterior portion of each atrium of the heart, increasing slightly the atrial volume http://faculty.ucc.edu/biology-potter/Fetal_Blood_Vessels Coronary Arteries & Cardiac Veins Right and Left Coronary Arteries - Supplies blood to the tissue of the heart Coronary Veins - Drain blood that passes through myocardial capillaries Coronary sinus - Empties into the right atrium Electrocardiogram (ECG) • Records the electrical changes that occur in the myocardium (heart muscle) during a cycle Pg 337 book • Why this works – Body fluids conduct electrical currents • Electrodes are placed on the skin & wires connected • The interment responds to low levels of electricity • Moves a pen up & down according to changes http://jlhuss.blog.lemonde.fr/ photos/uncategorized/ecg.gif Atrial Systole – Atria Contract Ventricular Diastole – Ventricles Relax Ventricular systole – Ventricles Contract Atrial diastole - Atria Relax Heart Sounds Sounds come from the vibrations in the heart tissues due to closing of the valves. Lubb-dupp 1) Lubb – Ventricular contraction (Systole) (Closing if the AV valves) 2) Dubb – Ventricular relaxation (Diastole) (Closing of the pulmonary and aortic valves) Blood Pressure • Pulse pressure – (also know as blood pressure) The force exerted against the inner wall of blood vessels • Mean arterial pressure - average arterial pressure during a single cardiac cycle – Can be used by doctors to help diagnose particular issues • Measure your lab partners blood pressure – Normal: Systolic = 120 (high140) (low 90) – Normal: Diastolic = 80 (high 90) (low 60) How to measure blood pressure Need a sphygmamanometer & a stethoscope Clean the ear pieces of the stethoscope Sit quietly and relaxed Place the cuff just above the elbow Wrap it snug but not tight Center the rubber bulb hose at the anterior of the arm Close the valve of the rubber bulb Next listen very carefully to me. Follow the instructions on page 282 of your lab manual http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/ap/dynamichuman2/content/gifs/0136A.gif