* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Este - Delmar
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
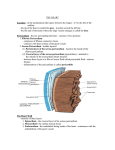
Chapter 16: Glossary Heart and Peripheral Vasculature Angina Angina is chest pain that occurs due to the imbalance between myocardial oxygen supply and myocardial oxygen demand. Apex The apex is the lower portion of the heart. Atrial kick Atrial kick (atrial systole) occurs when the atria contract and force the remaining 20% to 30% of blood into the ventricles. Atrioventricular (A-V) node The atrioventricular node is the back-up pacemaker of the heart. If the S-A node fails to initiate an impulse, the A-V node will take over. The A-V node has an intrinsic rate of 40 to 60 impulses per minute. Atrioventricular valves The atrioventricular valves are the mitral and tricuspid valves, which are located between the atria and the ventricles. The tricuspid valve is located between the right atrium and the right ventricle. The mitral valve is located between the left atrium and the left ventricle. Baroreceptors Baroreceptors, located in the carotid sinus, sense fluctuations in blood pressure and initiate compensatory responses (changes in heart rate, vasoconstriction). Base The base is the uppermost portion of the heart; it contains the left and right atria, the aorta, the pulmonary arteries, and the superior and inferior vena cavae. Bruit Bruits are blowing sounds heard when blood flow becomes turbulent in a blood vessel or when blood rushes past an obstruction. Click A click is an abnormal, high-pitched sound heard on systole. Crescendo Crescendo is a term used to describe sounds that go from soft to loud. Copyright © 2010 by Delmar, Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Decrescendo Decrescendo is a term used to describe sounds that go from loud to soft. Diastole Diastole is the phase of the cardiac cycle during which the myocardial fibers relax, allowing blood to fill the ventricles. Electrocardiogram An electrocardiogram records the electrical activity of the heart. Gallop A gallop is an additional sound that is best heard in early diastole at the apex of the heart. A gallop may or may not be an abnormal finding, depending on the patient's age and whether the patient is pregnant. Heaves A heave is a lifting of the cardiac area secondary to an increased workload. This is an abnormal finding. Hyperkinetic Hyperkinetic refers to an increased movement of pulsations (bounding pulse) in the mitral area. Hypokinetic Hypokinetic refers to a decreased movement of pulsations (weak pulse) in the mitral area. Infarction An infarction is a necrosis of the heart muscle caused by a lack of blood supply. Ischemia Ischemia is a local, temporary lack of blood supply to the heart. Orthostatic hypotension Orthostatic hypotension results when a patient's blood pressure significantly decreases and the heart rate increases as the patient moves from a lying down to a sitting or standing position. Pansystolic (holosystolic) A murmur that is audible throughout all of systole is referred to as a pansystolic or holosystolic murmur. Copyright © 2010 by Delmar, Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Parietal pericardium The parietal pericardium is the parietal layer of the pericardium that lies close to the fibrous tissues. Pericarditis Pericarditis is inflammation of the pericardium (the sac covering the heart). Precordium The precordium is the area on the anterior surface of the body overlying the heart, great vessels, pericardium, and pulmonary tissue. Septa The septa are vertical walls that divide the right and left atria and the right and left ventricles. Sinoatrial (S-A) node The sinoatrial node is the normal pacemaker of the heart. The intrinsic rate of the S-A node is between 60 and 100 impulses per minute. Snap A snap is an abnormal, high-pitched sound heard on diastole. Systole Systole is the phase of the cardiac cycle during which the myocardial fibers contract and tighten to eject blood from the ventricles. Thrills A thrill is a palpable vibration similar to what one feels when placing a hand on a purring cat. The presence of a thrill is an abnormal finding. Valve regurgitation Valve regurgitation is a backward flow of blood through the heart valve. Valve stenosis Valve stenosis is a narrowing or constricting of a diseased heart valve. Visceral pericardium The visceral pericardium is the visceral layer of the pericardium that covers the actual heart muscle. Copyright © 2010 by Delmar, Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.