* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Today`s Objectives
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
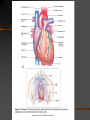
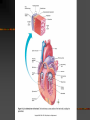
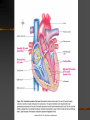
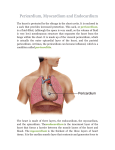
Today’s Objectives Be able to explain location, size and position of the heart Be able to explain the definitions Be able to label the pictures of the heart Heart:Location, Size, Position Located between the lungs and lower portion of mediastinum Two-thirds of its mass is on the left Triangular shape - a closed fist Thoracic cavity: between sternum in the front and the thoracic vertebrae behind Apex, lower edge, lies on the diaphragm Anatomy of the Heart Hollow, not solid Atria-upper chambers Ventricles-lower chambers Myocardium-cardiac muscle tissue that lines the walls of the chambers Interatrial septum- septum (divider) between the atrial chambers Interventricular septum-separates the ventricles Endocardium-thin layer of very smooth tissue that lines each chamber (“endo” means within or inside) Endocarditis-inflamed lining; rough and abrasive to RBC’s passing over its surface- thrombusfatal blood clot Pericardium – covering of the heart that consists of two layers of fibrous tissue: 1. Inner layer-epicardium (visceral pericardium) Covers the heart like skin on an apple (“epi” means upon or on) 2. Outer layer- parietal pericardium (loose fitting sac that allows the heart to beat) No friction because the two layers are moist serous membranes Pericardial fluid lubricates between heart and pericardial sac Pericarditis Inflammation of the pericardium Trauma, bacterial and viral infections, tumors Often visceral and parietal pericardium rub together – severe chest pain Pericardial effusion- pericardial fluid, pus, or blood accumulate in the space between the two layers and impairs pumping action of the heart Cardiac tamponade-compression of the heart Objectives 1. Be able to describe the conduction system of the heart 2. Be able to identify the structures of the heart involved in electrical conduction Conduction System of the Heart View the animation and take the quiz http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/ chapter22/animation__conducting_system _of_the_heart.html Conduction System of the Heart The intercalated disks are electrical connectors. Thus, both atrial walls will contract at about the same time and both ventricular walls will contract at about the same time. Conduction System Sequence 1. SA node (pacemaker) 2. All directions through atria causing atrial fibers to contract 3. AV node 4. Bundle of His 5. Purkinje fibers