* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology II – Chapter 4 Test**
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
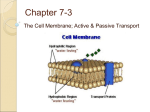
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Biology II – Chapter 4 Self Test 1. The outer living boundary of the cell is the _______________________________. 2. The cell membrane regulates the ____________________________ of molecules into and out of the cell 3. _____________________________ bilayer determines the basic structure of the cell membrane. 4. _____________________________ are cell-to-cell channels made of protein channels that connect the insides of adjacent cells. 5. _____________________________ is the transport that occurs constantly and is crucial in living organisms. 6. The lipid bilayer contains ____________________________ that have carbohydrate chains attached to the polar head. 7. The transfer of a substance into or out of a cell from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration by a process that requires a carrier and an expenditure of energy is known as _________________________________. 8. Energy is required to transport molecules against the concentration gradient in the form of _____________. 9. Because of the restricted passage associated with the cell membrane, it is said to be _________________________________. 10. Which of the following is a cell protein: recognition glycoprotein channel carrier all of these 11. Each phospholipid has a polar head that is __________________________, and two nonpolar tails that are _________________________________. 12. _________________________ proteins are required for facilitated diffusion and active transport. 13. The proteins which form pores or channels that selectively interact with specific molecules or ions so they can cross the membrane to enter or exit the cell are ___________________________ proteins. 14. ________________________________ is a type of transport that does not require any energy to occur. 15. _____________________________ is the type of passive transport that is spontaneous and no energy is required for it to begin. 16. Cell eating or the taking in of bacteria and/or debris by engulfing is known as _______________________. 17. A solution that has a higher concentration of solute and a lower concentration of water than the cell is called ____________________________. 18. ____________________________ proteins make up the cellular fingerprint or identification tag by which cells recognize each other. 19. Solutions where cells that are placed in them neither gain or lose water are _______________________. 20. Cell drinking or the taking in of fluid along with dissolved solutes by engulfing is known as ____________________________. 1 21. ________________________________________ selectively moves specific molecules into the cells with the aid of receptor proteins at coated pit sites. 22. Which of the following is NOT a passive transport: diffusion facilitated diffusion osmosis receptor-mediated endocytosis 23. _______________________________ is the cell connection that is restricted to plant cells. 24. The difference in net movement of a substance from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration is called the ______________________________________. 25. Glucose and amino acids cross the cell membrane even though they are not lipid soluble with help and no energy use by means of ___________________________________. 26. A process in which a vesicle is formed at the cell membrane to bring a substance into the cell is called _______________________________. 27. A process in which an intracellular vesicle fuses with the cell membrane so that the vesicle’s contents are released outside the cell is called ______________________________. 28. ____________________________ hold adjacent cells together through proteins filaments attached to the interior of each cell to further strengthen the attachment. 29. – 33. Label the following types of transports: Endocytosis Diffusion Osmosis Active Transport Passive Transport 2 KEY 1. cell membrane/plasma membrane 2. exchange 3. Phospholipid 4. gap junctions 5. Osmosis 6. glycoproteins 7. active transport 8. ATP 9. selectively permeable 10. all of these 11. hydrophilic, hydrophobic 12. carrier 13. channel 14. passive transport 15. diffusion 16. phagocytosis 17. hypertonic 18. Recognition 19. isotonic 20. pinocytosis 21. receptor-mediated endocytosis 22. receptor-mediated endocytosis 23. plasmodesmata 24. concentration gradient 25. facilitated diffusion 26. endocytosis 27. exocytosis 28. desmosomes 29.-33.Label the following types of transports: diffusion osmosis endocytosis Active transport Passive transport 3