* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study guide U-5 and 6 Essential Questions
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Osteochondritis dissecans wikipedia , lookup
X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency wikipedia , lookup
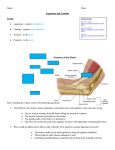
Study guide U-5 and 6 Essential Questions 1. What are the functions of skin? 2. What types of tissue make up the layers of the skin? 3. What role do accessory organs such as sweat glands and sebaceous glands play in the skin? 4. Which layers of the skin are damaged in different types of burns? 5. How does burn damage in the skin affect other functions in the body? 6. How do medical professionals in different fields assist with burn care and rehabilitation? 7. What role does pain play in the human body? 8. How does the body interpret and process pain? 9. Why would the inability to feel pain actually put the human body in danger? 10. How does the skeletal system assist with protection in the body? 11. How does the structure of compact bone differ from the structure of spongy bone? 12. What is an X-ray? 1. What are the different types of bone fractures? 2. How can damage to a bone affect other human body systems? 3. What is bone remodeling? 4. How do osteoblasts and osteoclasts assist with bone remodeling and overall bone homeostasis? 5. What is the relationship between bone remodeling and blood calcium levels? 6. What are the four main stages of healing that occur after a bone fracture? 7. What body systems function to protect the human body? 8. What is an antigen? 9. What is an antibody? 10. What is specific immunity? Key Terms Collagen An insoluble fibrous protein of vertebrates that is the chief constituent of the fibrils of connective tissue (as in skin and tendons) and of the organic substance of bones. Connective Tissue Animal tissue that functions mainly to bind and support other tissues, having a sparse population of cells scattered through an extracellular Dermis Elastin Endorphin Epidermis Epithelium Exocrine gland First-degree burn Keratin Melanin Pain Sebaceous gland Second-degree burn Third-degree burn Bone marrow Calcitonin Callus Compact bone Diaphysis matrix. The sensitive vascular inner mesodermic layer of the skin. A protein that is similar to collagen and is the chief constituent of elastic fibers. A hormone produced in the brain and anterior pituitary that inhibits pain perception . The outer nonsensitive and nonvascular layer of the skin of a vertebrate that overlies the dermis. A membranous cellular tissue that covers a free surface or lines a tube or cavity of an animal body and serves especially to enclose and protect the other parts of the body, to produce secretions and excretions, and to function in assimilation. A gland (as a sweat gland, a salivary gland, or a kidney) that releases a secretion external to or at the surface of an organ by means of a canal or duct. A mild burn characterized by heat, pain, and reddening of the burned surface but not exhibiting blistering or charring of tissues. Any of various sulfur-containing fibrous proteins that form the chemical basis of epidermal tissues (as hair and nails) and are typically not digested by enzymes of the gastrointestinal tract. Any of various black, dark brown, reddish brown, or yellow pigments of animal or plant structures (as in skin and hair). Basic bodily sensation that is induced by a noxious stimulus, is received by naked nerve endings, is characterized by physical discomfort (as pricking, throbbing, or aching), and typically leads to evasive action. Any of the small sacculated glands lodged in the substance of the derma, usually opening into the hair follicles, and secreting an oily or greasy material composed in great part of fat which softens and lubricates the hair and skin. A burn marked by pain, blistering, and superficial destruction of dermis with edema and hyperemia of the tissues beneath the burn. Severe burn characterized by destruction of the skin through the depth of the dermis and possibly into underlying tissues, loss of fluid, and sometimes shock. A soft highly vascular modified connective tissue that occupies the cavities and cancellous part of most bones and occurs in two forms – yellow and red. A polypeptide hormone especially from the thyroid gland that tends to lower the level of calcium in the blood plasma. A growth of new bone tissue in and around a fractured area, ultimately replaced by mature bone. Bone tissue that contains few spaces between osteons; forms the external portion of all bones and the bulk of the diaphysis (shaft) of long bones. The shaft of a long bone. Epiphysis Fracture Osteoblast Osteoclast Osteocyte Parathyroid hormone Spongy (cancellous) bone Agglutination Alleles Antibody Antigen B lymphocyte (B cell) Lymph Lymph node Lymphocyte Macrophage Pedigree T lymphocyte (T cells) Intervention The end of a long bone, usually larger in diameter than the shaft. The breaking of hard tissue (as bone). A bone-forming cell. Any of the large multinucleate cells closely associated with areas of bone resorption (as in a fracture that is healing). Cell that is characteristic of adult bone and is isolated in a lacuna of the bone substance. A hormone of the parathyroid gland that regulates the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus in the body. Bone tissue that consists of an irregular latticework of thin plates of bone called trabeculae; found inside short, flat, and irregular bones and in the epiphyses of long bone. Clumping of microorganisms or blood cells, typically due to an antigenantibody interaction. Alternate forms of a single gene that control the same inherited trait (such as type A blood) and are located at the same position on homologous chromosomes. An antigen-binding immunoglobulin, produced by B cells, that functions as the effector in an immune response. A foreign macromolecule that does not belong to the host organism and elicits and immune response. A type of lymphocyte that develops in the bone marrow and later produces antibodies, which mediate humoral immunity. A usually clear fluid that passes from intercellular spaces of body tissue into the lymphatic vessels, is discharged into the blood by way of the thoracic duct and right lymphatic duct, and resembles blood plasma in containing white blood cells and especially lymphocytes but normally few red blood cells and no platelets. Any of the rounded masses of lymphoid tissue that are surrounded by a capsule of connective tissue, are distributed along the lymphatic vessels, and contain numerous lymphocytes which filter the flow of lymph passing through the node. Any of the colorless weakly motile cells that originate from stem cells and differentiate in lymphoid tissue (as of the thymus or bone marrow), that are the typical cellular elements of lymph, that include the cellular mediators of immunity, and that constitute 20 to 30 percent of the white blood cells of normal human blood. An amoeboid cell that moves through tissue fibers, engulfing bacteria and dead cells by phagocytosis. A diagram of a family tree showing the heritable characters in parents and offspring over multiple generations . A type of lymphocyte responsible for cell-mediated immunity that differentiates under the influence of the thymus. Any measure whose purpose is to improve health or alter the course of disease.