* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
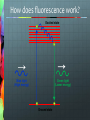
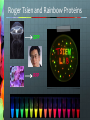
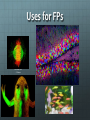
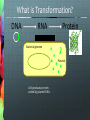
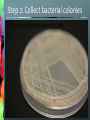
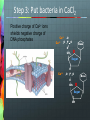
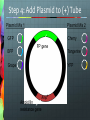
Announcements New Weekly Schedule Observer on March 6 and 13 Measuring Zone of Inhibition Bacterial Transformation Student Training By Quanina Quan and UCSD ScienceBridge Objective Demonstrate that changes in genotype causes changes in phenotype by transforming E.coli into fluorescent E.coli. Background What is E.coli? A rod shaped bacterium found in our lower intestines What is fluorescence? A substance that absorbs light at one wavelength (UV) and re-emits light at a visible wavelength (color) Background: What is GFP? Green Fluorescent Protein Chromophore How does fluorescence work? Excited state Blue light (High energy) Green light (Lower energy) Ground state NOTE: FLUORESCENCE IS NOT LUMINESCENCE Fluorescence: Absorbs light at one wave length and emits it at another Bioluminescence: Produces its own light A Metaphor Fluorescence: Absorbs light at one wave length and emits it at another Bioluminescence: Produces its own light Fluorescent Organisms Fluorescence: Absorbs light at one wave length and emits it at another Roger Tsien and Rainbow Proteins GFP RFP Uses for FPs Human Cell J. Waters FAQs Can I make myself or someone I know glow? Can I get a glowing pet? Can we turn it on or off? What is a plasmid? • A small circular piece of DNA • Naturally occurring • Can be altered in lab to express protein of interest What is Transformation? DNA RNA Protein E. coli bacterial cell Bacterial genome Plasmid Cell produces protein coded by plasmid DNA. How We Make E.coli Glow Plasmid Uptake of foreign DNA, often a circular plasmid Allow bacteria to grow for 1-3 days DNA RNA Protein Bacteria now express cloned fluorescent protein… What’s on the plasmid Plasmid Mix 1 Plasmid Mix 2 GFP Cherry FP gene BFP Tangerine Grape YFP AmpR Ampicillin resistance gene How the Plasmid Gets in the Bacteria Show Video 1. Add CaCl2 2. Heat/Shock Step 0: Label Plates Step 1: Put CaCl2 in Tube Step 2: Collect bacterial colonies “Like scraping whipped cream off of Jello.” Step 3: Put bacteria in CaCl2 Positive charge of Ca2+ ions shields negative charge of DNA phosphates Ca++ Ca++ O O P O O CH2 Base O Sugar O Ca++ O P O O Base O CH2 Sugar OH Step 4: Add Plasmid to (+) Tube Plasmid Mix 1 Plasmid Mix 2 GFP Cherry FP gene BFP Tangerine Grape YFP AmpR Ampicillin resistance gene Step 5: Heat Shock! • Incubate on ice to slow fluid cell membrane • Heat-shock increases permeability of membranes Leave in heat 45 seconds!!! - Too short, and bacteria won't let in plasmid. - Too long, and the bacteria will die. ICE – HEAT – ICE Step 6: Plate on Ampicillin • Ampicillin inhibits cell wall growth. • Only cells that can inactivate the ampicillin around them will grow. • Ampicillin resistance is tied to (expressed with) the fluorescent protein gene. • Ampicillin is a selection mechanism that only allows transformed bacteria to grow on the plate. We have two controls LB only (-) = Control 1: check for viable cells LB amp (-) = Control 2: check for ampicillin function LB amp (+) = Experimental plate: grow transformants Why Ampicillin? LB/AMP + LB/AMP - Why Ampicillin? LB/No Amp Tricky Parts of Lab Labeling Plates Getting Bacteria Pipetting the right amount Plating FAQ Why don’t I see anything glowing right now?