* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download History of Life - CHS
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Origin of language wikipedia , lookup
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral modernity wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Before the Dawn (book) wikipedia , lookup
Abiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
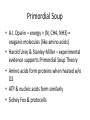
History of Life (Chapter 14) The Record & Origin of Life Earth’s History Geologic Timescale – calendar of Earth’s history based on rocks & fossils 4 Eras: • Precambrian • Paleozoic • Mesozoic • Cenozoic http://lifeasahuman.com/files/2011/01/geological-time-scale.jpg Plate Tectonics – movement of land masses • Helps to explain why similar fossils are found on different continents • May account for speciation • VERY gradual • http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/geology/anim1.html Fossils – evidence of an organism from long ago • • • • Provide record of life on Earth Imprint, burrow, actual bone Demonstrate diversity Evidence of behavior Photography by J. Botz & K. Williams Biogenesis vs Spontaneous Generation http://www.expertsmind.com/questions/theory-of-biogenesis-30116598.aspx How did life begin? • • • • • Divine Origins (theology) Meteorites (semantics) Primordial Soup (re-create organic molecules) Bubbles (1986, supports Primordial Soup) “An RNA World” (self-replicating molecules preceded self-replicating organisms) Primordial Soup • A.I. Oparin – energy + (N, CH4, NH3) = oraganic molecules (like amino acids) • Harold Urey & Stanley Miller – experimental evidence supports Primordial Soup Theory • Amino acids form proteins when heated w/o O2 • ATP & nucleic acids form similarly • Sidney Fox & protocells Bubbles • Louis Lerman (1986) suggest primordial soup occurred in tiny bubbles of lipid molecules. • Wind, waves, rainfall created bubbles • Bubbles provided environment to speed reactions of primordial soup “An RNA world” • • • • Self-replicating molecules preceded cells DNA, RNA (perhaps a precursor?) RNA probably predated DNA Difficult to obtain data to support this idea because RNA is more complex than a protein (like what was produced in Primordial Soup experiments) “First” is still a mystery, but early development well supported… • Small organic molecules can form complex organic molecules • Earliest: anaerobic, heterotrophic, prokaryotes • Next: chemosynthetic prokaryotes (similar to archaebacteria) • Then: photosynthetic prokaryotes (produced O2) • Evolution of aerobic cells & eukaryotes (endosymbiont hypothesis) Evolution & Natural Selection (Chapter 15) Natural Selection • • • • • • • Charles Darwin Artificial selection (breeding) Mechanism for change in populations Adaptations (structural, behavioral) “survival of the fittest” Camouflage Mimicry Evidence for Evolution • Field observations (some laboratory, too) • Fossil record • Anatomy – Homologous structures – Vestigial structure (no current function, but functioned in ancestor) – Analogous structures (not direct support) • Biochemistry • Embryology (tail & gill slits in embryos) Haekel’s drawings http://ncse.com/book/export/html/11831 Mechanisms for Evolution • A gene pool w/ allelic frequencies that remain constant through generations demonstrates genetic equilibrium • Evolution occurs only when genetic equilibrium changes – Mutation (when useful, gains prominence in gene pool) – Genetic drift (chance events alter allelic frequency) – Gene flow (individuals move in & out of population) • Natural selection acts on variation and usually factors into changes in established gene pools • Speciation – Isolation: Geographic, reproductive – Gradualism & Punctuated Equilibrium Selection & Patterns of Evolution • Natural Selection – Stabilizing selection (favors average) – Directional selection (favors one extreme) – Disruptive selection (favors extremes) • Diversity – Adaptive radiation (“branches”) – Divergent evolution (distinct from ancestor) – Convergent evolution (distant relatives evolve similar traits) Primate Evolution (Chapter 16) Primate Adaptation & Evolution Human Ancestry Primate Adaptation & Evolution • Primate = arboreal mammals • Primate Adaptations: – Binocular vision – Opposable thumbs – Flexible joints (hips & shoulders) – Complex brains – How might these adaptations be beneficial for life in the trees? Primate Adaptation & Evolution • Primates appear in fossil record 65-70 mya • Trends: – Increasing brain size http://www.athenna.com/dr-peppers-evolution-joke-on-facebookriles-up-creationists/athenna/web_design/teoria-de-design/ – Walking upright Primate Adaptation & Evolution (two groups) Prosimians • Small, noctournal • Tropical environments • Lemurs • Tarsiers Anthropoids • Monkeys – New World • Prehensile tail – Old World • No tail • Hominoids (apes & humans) – Long-term parental care – Social Human Ancestry • Humans developed over time – Brain & body size increased – Bipedalism more efficient – Jaws & teeth decrease in size Human Ancestry (great pic 445) • Earliest hominids arose in Africa • (hominids = primates that can walk upright on 2 legs – gorillas, chimps, bonobos, humans) – 5-8 mya (last common ancestor w/ apes 5-10 mya) – Old world monkeys became adapted to global cooling (new climate conditions) – Probable order • Gibbons • Orangutans • Chimps & gorillas (likely share human ancestor) Human Ancestry • Sahelanthropus tchadensis – oldest known hominid (or near hominid) 6-7 mya (2002) • Ardipithecus ramidus 4.4 mya (1994) – indicate bipedalism evolved in forested areas, not open savannah • Australopithecus anamensis ~ 4 mya (1995) • Australopithecus afarensis 3-4 mya (1974) “Lucy” • *other Australopithecus species lived between 4 and 1 mya (http://www.talkorigins.org/faqs/homs/species.html) Human Ancestry • Homo habilis 2.5-1.1 mya, “handy man” rudimentary speech? • Homo erectus 1.8 million – 300K yrs ago “upright human” hunting & fire? • Homo antecessor 780 K yrs ago (1977) earliest European hominid Human Ancestry • Homo sapiens appeared in Europe, Africa, Middle East, Asia (400-100 kya, book) • Homo sapiens (archaic) (also Homo heidelbergensis) 500-200 kya (H. erectus similar) • Homo sapiens neanderthalensis (also Homo neanderthalensis) 230-30 kya • Homo sapiens sapiens (modern) 195 kya – Continue to see trends toward small molars & less robust Human Ancestry • Stone tools coincide w/ genus Homo in fossil record – Homo Habilis – first evidence of tool use – Neanderthal • Genetic evidence suggested NOT evolve to Cro-Magnon (may have interbred, however) – Cro-Magnon – spread throughout Europe 35-40 kya • 200 kya: Africa, Europe, Asia • 12 kya: North America • 8-10 kya Native Americans had agriculture & domestication