* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 21.1 Plant Cells and Tissues
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
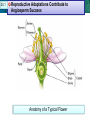
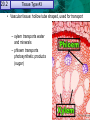
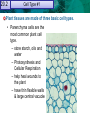
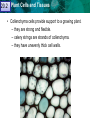
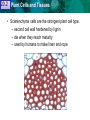
Reproductive Adaptations Contribute to 20.1 21.1 Plant Cells and Tissues Angiosperm Success Anatomy of a Typical Flower 20.1 21.1 Reproductive Adaptations Plant Cells and TissuesContribute to Angiosperm Success Adaptations: • • • • Sepals Petals Stamen Carpal/Pistil 20.1 21.1 Plant Cells and Tissues Adaptations • Double Fertilization – Embryo – Endosperm Embryo • Seeds – Seed coat – Embryo – Cotyledon 20.1 21.1 Plant Cells and Tissues Asexual Reproduction In Angiosperms • Vegetative Reproduction: dropped stems or shoots that establish new roots and become clones. 20.2 21.1 Plant Cells and Tissues KEY CONCEPT Plants have specialized cells and tissue systems. 20.2 21.1 Plant Cells and Tissues A Plant’s Roots and Shoots System • Root system – Fibrous Root vs Tap Root • Shoot system – Stems 20.2 Tissue Types & #2 21.1 Plant Cells and#1Tissues Plant organs are made of three tissue systems. • Dermal tissue covers the outside of a plant. – protects the plant stem – secretes cuticle of leaves – forms outer bark of trees • Ground tissue is found inside a plant. – provides support – stores materials in roots and stems – Photosynthesis (in the shoot) leaf root Tissueand TypeTissues #3 20.2 21.1 Plant Cells • Vascular tissue: hollow tube shaped, used for transport – xylem transports water and minerals – phloem transports photosynthetic products (sugar) Cell Type 20.2 21.1 Plant Cells and #1 Tissues Plant tissues are made of three basic cell types. • Parenchyma cells are the most common plant cell type. – store starch, oils and water – Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration – help heal wounds to the plant – have thin flexible walls & large central vacuole 21.1 20.2 Plant Cells and Tissues • Collenchyma cells provide support to a growing plant. – they are strong and flexible. – celery strings are strands of collenchyma. – they have unevenly thick cell walls. 20.2 21.1 Plant Cells and Tissues • Sclerenchyma cells are the strongest plant cell type. – second cell wall hardened by lignin – die when they reach maturity – used by humans to make linen and rope