* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download positive selection - immunology.unideb.hu
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Major histocompatibility complex wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
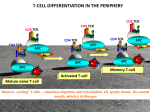
DIFFERENTIATION AND MATURATION OF T CELLS IN THE THYMUS REGULATED T-CELL DIFFERENTIATION preT- CD4+CD8+ TCR APC Epithelial cell immature T cell pre T cell pro T cell SIGNALING RECEPTOR NO ANTIGEN RECOGNIZING RECEPTOR ANTIGEN RECOGNIZING RECEPTOR Lymphoid precursor T- CELL DEVELOPMENT NK cell No rearrangement c-kit/CD44 RAG-1/RAG-2 Pro-T -rearrangement Pre-T H rearrangement Pre-T -rearrangement Surrogate L Pre-B L rearrangement T B Selection clonal deletion Selection clonal deletion B T B T Mature-T Pro-B T B Mature-B EVENTS OF T CELL DIFFERENTIATION IN THE THYMUS 1. Generation of NK cells – no TCR 2. Differentiation of γδ and αβ TCR carrying T cells 3. Selection of αβ TCR – positive selection – negative selection 4. Differentiation of CD4+ and CD8+ T cell lineages γδ T-cell No selection Pro-T Early pre-T Pre-Tαchain Lck signal IL-7-dependent proliferation β rearrangement unsuccesful βchain Late pre-T CD4+CD8+ α rearrangement αβ NKT-cell CD4+CD8+ αβCD4+ αβCD8+ unsuccesful α-chain no positive selection negative selection SELECTION OF T LYMPHOCYTES IN THE THYMUS UNDER THE CAPSULE IL-7-dependent proliferation CORTEX CD4-CD8DN β+preTα TCRαβ CD4+CD8+ TCR(-) sMHC+sP sMHC+fP fMHC+fP DP selection CORTEX/ MEDULLA + + NO MEDULLA – AICD αβTCR CD4+ – selection 1. The primary T cell pool is biased to MHC-specificity (V genes) 1-2% for one allotype 2. Focusing the T cell pool to self MHC recognition (+) 3. Elimination of useless and self agressive clones (-) 4. CENTRAL TOLERANCE 5. Focusing the T cell repertoire for recognition of non self 6. CD4+ and CD8+ T cell use the same TCR repertoire 7. Individualized T cell repertoire available in the periphery 8. CD4 and CD8 co-stimulatory molecules are involved in positive selection AICD – Activation Induced Apoptosis αβTCR CD8+ PERIPHERAL TOLERANCE POSITIVE SELECTION OF DOUBLE POSITIVE (DP) T CELLS ALSO DIRECTS CD4 AND CD8 SINGLE POSITIVE (SP) T CELL COMMITMENT CD4+CD8+ CD4+CD8+ Thymic epithelial cell MHC-I + peptide complexes recruit CD8 MHC-II + peptide complexes recruit CD4 POSITIVE SELECTION FOR 3 – 4 DAYS, SUCCESSIVE α-GENE REARRANGEMENTS BARE LYMPHOCYTE SYNDROME (BLS) Lack of MHC class I – no CD8+ cells Lack of MHC class II – no CD4+ cells SELECTION OF THE T CELL REPERTOIRE – CENTRAL TOLERANCE POSITIVE SELECTION – Thymic education (no instruction for specificity) Low avidity interaction of MHC - self peptide - TCR Thymic epithelial cells Self peptide composition and concentration (foreign peptides are not present) Low peptide dose induces positive selection – special ligands 80-90% of DN (CD4-CD8-) T cells is NOT positively selected PASSIVE CELL DEATH BY NEGLECTION NEGATIVE SELECTION – Central self tolerance High avidity of MHC - self peptide - TCR interaction Ubiquitous and abundant self antigens are present in the thymus High peptide dose induces negative selection Any thymic antigen presenting cell: epithelial cells, bone marrow-derived macrophages, dendritic cells THE GENERATION OF SELF MHC + FOREIGN PEPTIDE SPECIFIC T CELLS REQUIRES WEAK INTERACTION WITH SELF MHC + SELF PEPTIDE SELF RESTRICTED AND TOLERANT PERIPHERAL T CELL REPERTOIRE PHYSIOLOGICAL TRESHOLD NOT COMPLETE HOMEOSTASIS OF POSITIVE AND NEGATIVE SELECTION IN THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE AVAILABLE T LYMPHOCYTE REPERTOIRE Homozygote Heterozygote Ratio of negative selection increases with the number of MHC genes Ratio of positive selection Number of MHC molecules T-CELL DIFFERENTIATION IN THE PERIPHERY CD8 TCR CD8 TCR CD8 TCR CD4 TCR CD4 TCR APC APC CD4 TCR APC Ag Ag Ag APC APC Memory T-cell Activated T-cell Mature naive T-cell APC PERIPHERAL TOLERANCE IMMUNE RESPONSES ARE NOT INITIATED IN THE PERIPHERY Normal tissue cells do not express MHC class II NO SIGNAL 1. for CD4+ Th activation Normal tissue cells do not express co-stimulatory molecules and do not produce T cell differentiating cytokines NO SIGNAL 2. for CD4+ Th activation Migration of naive T lymphocytes to normal tissues is limited Antigen presenting cells are not activated in normal tissues NO SIGNAL 3. for CD4+ Th activation PERIPHERAL TISSUES TOLERIZE THEMSELVES MECHANISMS OF PERIPHERAL TOLERANCE ANERGY – Functional unresponsiveness, no IL-2 secretion SIGNAL 1 SIGNAL 2 SIGNAL 3 Recognition of auto-antigen on tissue cell No B7 and CD40 expression, no co-stimulation Tissue resident professional APC are not activated Innate immunity is not activated No inflammation CLONAL DELETION – Activation induced cell death Requires persistant high antigen dose Fas – FasL interaction SUPPRESSION – Activity of other cells Cytokine-mediated balance Effector functions are inhibited by regulatory T cells CLONAL IGNORANCE No contact with the immune system Immunologically privileged sites Central nervous system, eye No recognition in the periphery Arming of effector T cells Clonal selection and differentiation APC T Activation of NAÏVE T cells by signal 1 and 2 is not sufficient to trigger effector function, but….. the T cell will be activated to proliferate and differentiate under the control of autocrine IL-2 to an effector T cell. These T cells are ARMED IL-2 Effector T cell How can this cell give help to or kill cells that express low levels of B7 family costimulators? Effector function or Anergy? Clonally selected, proliferating and differentiated T cell sees antigen on a B7 negative epithelial cell The effector programme of the T cell is activated without costimulation Armed Effector T cell Armed Effector T cell IL-2 This contrasts the situation with naïve T cells, which are anergised without costimulation Naïve T cell CD28 TcR Co-receptor Kill Epithelial cell Epithelial cell Epithelial cell