* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MILITA ROY BEJOY NARAYAN MAHAVIDYALAYA
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
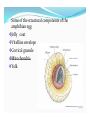
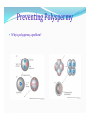
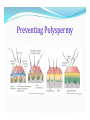
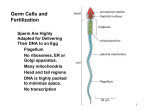
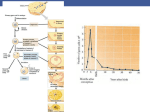
MILITA ROY BEJOY NARAYAN MAHAVIDYALAYA SPERM FORMATION Maturation of a sperm cell- 1. Nucleus is condensed 2. Acrosome is formed 3. Neck piece and tail piece is formed: formation of flagellum from centriole Body elongated and become streamlined by discarding the excess cytoplasmic material Ultrastructure of flagella: Flagella contribute to sperm motility protofilaments consist of tublulin dimers histone H1 stabilizes flagellar microtubules dynein, attached to microtubules hydrolyzes ATP, ATP comes from mitocondria in midpiece sliding of outer doublet Egg Egg attain the large size due to accumulation of the following necessary materials yolk proteins ribosomes t-RNA m-RNA morphogenic factors protective chemicals Some of the structural components of the amphibian egg Jelly coat Vitelline envelope Cortical granule Mitochondria Yolk Sperm enters at various stages of meiotics division of the egg of different animals Sperm Attraction Chemotaxis Movement toward a chemical, gradient is followed In Arbacia punctulata – the effects of adding resact to sperm suspension resact isolated from egg jelly is depicted in the picture 1 2 3 4 Sperm Attraction What is a sperm-activating peptide? RESACT- the 14 peptide amino acid is responsible for chemotaxis. Causes increases in sperm respiration and motility via a signal transduction mechanism. Sperm – Egg Interaction The acrosomal reaction in sea urchins: Acrosomal membrane is fused with the sperm plasma membrane , enzymes are released. Components of egg jelly bind to receptors on sperm cell membrane Calcium channels opened, calcium enters sperm head and induces fusion of acrosomal vesicle with membrane leading to exocytosis of enzymes Acrosomal process forms from polymerization of actin also facilitated by calcium Sperm – Egg Interaction The bindin protein (present on the inner membrane of acrosome) are now at the tip of the sperm and plays an important role in species specific recognition. Sperm – Egg Interaction Polymerization of egg actin leads to formation of fertilization cone, helps for fusion. Sperm – Egg Interaction in mammals contact occurs on side of sperm head; CD9 associated integrin protein in egg needed for fusion along with fertilin in sperm Preventing Polyspermy Why is polyspermy a problem? Preventing Polyspermy Preventing Polyspermy Fertilization membrane is formed from the fusion of Cortical granules with the plasma membrane of egg. The internal enzymes ( such as Hyaleuronidase, Peroxidase) and hyalin are released which form the membrane. The membrane is a permanent structure and a permanent solution to the problem of polyspermy. Egg Activation increase in calcium levels trigger many reactions – can block with EGTA can activate artificially using calcium ionophore most protein synthesis comes from stored mRNA by removing an inhibitor Egg Activation signaling pathway releases intracellular calcium ion concentration Fusion of Genetic Material DNA & centriole forms initial spindle for division. sperm nucleus decondensed to form pronucleus – involves phosphorylation of lamin protein in envelop and two sperm histones can fuse with egg pronucleus. lengthy process – sperm DNA bound to protamines in compacted form – glutathione breaks dissulfide bonds to de-compact DNA; when sperm enters egg hasn’t complete meiosis; DNA synthesis occurs separately in each pronucleus; true diploid nucleus doesn’t form untill 2-cell stage Rearrangement of Egg Cytoplasm Cytoplamic rearrangement occurs as a result of fertilization : Parallel microtubles between cortical and inner cytoplasm appear responsible for movement