* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download bio 342 human physiology
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
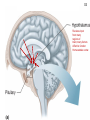
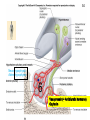
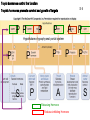
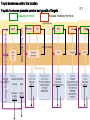
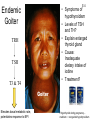
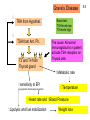
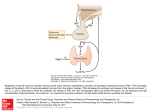
Monday, 19 September Chapter 11 The Endocrine System Two 1QQs returned on Piano Lab this week: Analyzing a research paper + First Endocrine Case study. Lab next week: Four more cases in endocrinology Pick up your photocopy from the Piano, read it before lab! King DS, Sharp RL, Vukovich MD, Brown GA, Reifenrath TA, Uhl NL, Parsons KA . Effect of oral androstenedione on serum testosterone and adaptations to resistance training in young men: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 1999; 281(21):2020-8 Wednesday, 21 September Chapter 6 The Nervous System Read sections A and B 1QQ # 6 for 8:30 Write the number of the one question you choose to answer. 1. a) b) c) d) e) 2. a) b) c) d) e) TSH stimulates The thyroid gland to take up iodide the synthesis and secretion of thyroglobulin The uptake of thyroglobulin from the colloid Follicular cells of the thyroid gland to grow The hypothalamus to secrete more TRH. OR In response to a drop in blood pressure Juxtaglomerular cells of the kidney secrete less renin Elevated levels of aldosterone stimulate thirst Newly-formed angiotensin I causes vasoconstriction Elevated levels of aldosterone promote Na+ retention by the kidneys The liver produces more Angiotensin II. 1QQ # 6 for 9:30 Write the number of the one question you choose to answer. 1. a) b) c) d) e) 2. a) b) c) d) e) TSH stimulates The thyroid gland to take up iodide the synthesis and secretion of thyroglobulin The uptake of thyroglobulin from the colloid Its target cells to incorporate more Na+/K+ ATPase into their membranes The hypothalamus to secrete more TRH. OR In response to a drop in blood pressure Juxtaglomerular cells of the kidney secrete less renin Elevated levels of Angiotensinogen stimulates thirst Newly-formed angiotensin I causes vasoconstriction Elevated levels of aldosterone promote Na+ retention by the kidneys The liver produces more Angiotensin II. S3 Fig. 11.12a Receives input from many regions of brain; many factors Affect its function Homeostatsis center. S4 Fig. 11.12b Neurohypophysis Adenohypophysis 6 Vasopressin (= Antidiuretic hormone) Oxytocin Tropic hormones control the function S6 Trophic hormones promote survival and growth of targets P P P P A P Hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal system P P S P P P A Releasing Hormone Release-inhibiting Hormone P S Tropic hormones control the function Trophic hormones promote survival and growth of targets Short-loop Neg. Feed. Long-loop negative feedback Releasing Hormone Release Inhibiting Hormone S7 Who Cares? S4 • Symptoms of hypothyroidism • Levels of TSH and TH? • Explain enlarged thyroid gland • Cause: Inadequate dietary intake of iodine • Treatment? Endemic Goiter TRH TSH T3 & T4 Goiter Elevates basal metabolic rate, potentiates response to EPI If hypothyroid during pregnancy… cretinism = congenital hypothyroidism Classification of Endocrine disorders • Hypersecretion – Primary – Secondary • Hyposecretion – Primary – Secondary hypothalamus CRH Anterior pituitary ACTH Adrenal Cortex Cortisol S3 Who else Cares? Aunt Dot S5 Grave’s Disease ⇩ ⇩ TRH from Hypothal. TSH from Ant. Pit. T3 and T4 from Thyroid gland ⇧sensitivity to EPI (up-regulation of adrenergic receptors) Blood test: TSH levels low TH levels high The cause: Abnormal Immunoglobulins in patient activate TSH receptors on Thyroid cells ⇧Metabolic rate ⇧Temperature ⇧Heart rate and ⇧Blood Pressure ⇧Lipolysis and fuel mobilization Weight loss S6 Grave’s Disease Treatment: Radioactive Iodine Mechanism:…….. S7 Vasopressin Cytokines from immune cells CRH from Hypothalamus ACTH from Ant. Pit S8 Physical trauma Prolonged exposure to cold Prolonged intense exercise Infection Sleep deprivation Pain Fright Emotional distress Basal levels of Cortisol Required for normal sensitivity to EPI; symptoms of excess cortisol are….. Clinical example: treatment of chronic inflammation (e.g. arthritis) can lead to Cushing’s Syndrome! ⇧Cortisol secretion from Adrenal Cortex Mobilize fuel from muscle & adipose tissue Suppress non-essential functions (reproduction & growth) Suppress inflammatory & immune responses Potentiates response to EPI (vascular smooth muscle) Cushing’s Syndrome Excess Cortisol from 1) adrenal cortex tumor (primary) or 2) hypersecretion of ACTH from anterior pituitary (secondary)