* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download lower limb bones - ugur baran kasirga web pages
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
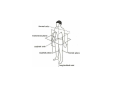
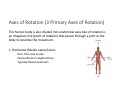
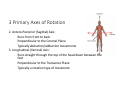
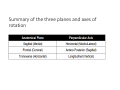
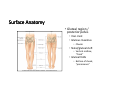
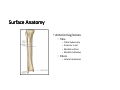
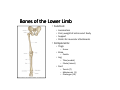
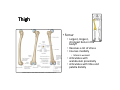
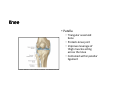
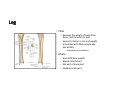
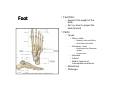
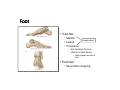
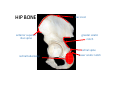
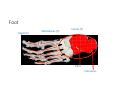
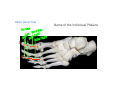
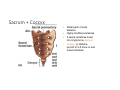
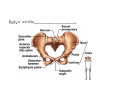
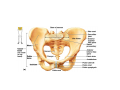
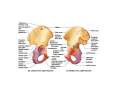
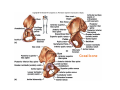
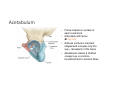
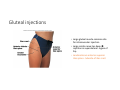
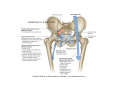
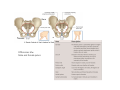
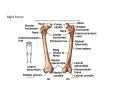
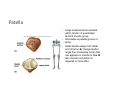
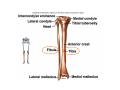
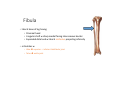
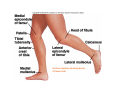
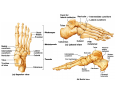
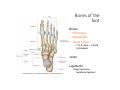
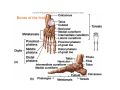
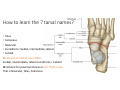
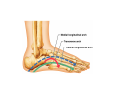
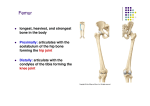
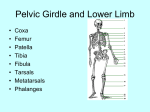
LOWER LIMB BONES Today’s Study Plan: Review of General Anaomical Topics Review of Upper Limb bones Lower Limb bones Quiz Lab hour Quiz Anatomical Position • • Anatomists and physiologist look at the human body from this standard starting point known as the anatomical position. • • The human body standing erect • Face facing forward • Arms by the sides • Palms facing forward • Legs straight • Feet flat on the floor and turn out very slightly Anatomical Planes The anatomical position is further standardized by dividing the body into three anatomical planes. A plane is an imaginary flat surface passing through the body or organ which divides the structure. 1) Frontal (Coronal) Plane: is vertical and extends from one side of the body to the other. It divides the body into front and back sections. 2) Sagittal (Medial) Plane: is vertical and extends from the front of the body to the back. It divides the body into right and left sections. 3) Transverse (Horizontal) Plane: is horizontal and divides the body into upper and lower segments. What is «Right angle»? What is «Perpendicular»? Axes of Rotation (3 Primary Axes of Rotation) The human body is also divided into anatomical axes Axis of rotation is an imaginary line (point of rotation) that passes through a joint or the body to describe the movement. 1. Horizontal (Medio-Lateral) Axis: Runs from side to side Perpendicular to Sagittal Plane Typically flexion/extension 3 Primary Axes of Rotation 2. Antero-Posterior (Sagittal) Axis: Runs from front to back Perpendicular to the Coronal Plane Typically abduction/adduction movements 3. Longitudinal (Vertical) Axis: Runs straight through the top of the head down between the feet Perpendicular to the Transverse Plane Typically a rotation type of movement Summary of the three planes and axes of rotation QUO VADIS? Surface Anatomy • Gluteal region / posterior pelvis • Iliac crest • Gluteus maximus • Cheeks • Natal/gluteal cleft • Vertical midline; “Crack” • Gluteal folds • Bottom of cheek; “prominence” Surface Anatomy • Anterior leg bones • Tibia • • • • Tibial tuberosity Anterior crest Medial surface Medial malleolus • Fibula • Lateral malleolus Bones of the Lower Limb • Function: • • • • Locomotion Carry weight of entire erect body Support Points for muscular attachments • Components: • Thigh • Femur • Knee • Patella • Leg • Tibia (medial) • Fibula (lateral) • Foot • Tarsals (7) • Metatarsals (5) • Phalanges (14) Thigh • Femur • Largest, longest, strongest bone in the body!! • Receives a lot of stress • Courses medially • More in women! • Articulates with acetabulum proximally • Articulates with tibia and patella distally Knee • Patella • Triangular sesamoid bone • Protects knee joint • Improves leverage of thigh muscles acting across the knee • Contained within patellar ligament Leg • Tibia • Receives the weight of body from femur and transmits to foot • Second to femur in size and weight • Articulates with fibula proximally and distally • Interosseous membrane • Fibula • • • • Does NOT bear weight Muscle attachment Not part of knee joint Stabilize ankle joint Foot • Function: • Supports the weight of the body • Act as a lever to propel the body forward • Parts: • Tarsals • Talus = ankle • Between tibia and fibula • Articulates with both • Calcaneus = heel • Attachment for Calcaneal tendon • Carries talus • Navicular • Cuboid • Medial, lateral and intermediate cuneiforms • Metatarsals • Phalanges Foot • 3 arches • Medial • Lateral • Transverse Longitudinal • Has tendons that run inferior to foot bones • Help support arches of foot • Function • Recoil after stepping Appendicular Skeleton Pelvic Girdle and Lower Limb Sacrum ilium sacroiliac joint iliac fossa ischium acetabulum pubis pubic symphysis Pelvic Girdle obturator foramen HIP BONE anterior superior iliac spine iliac crest greater sciatic notch ischial spine ischial tuberosity lesser sciatic notch Anterior Femur head patellar surface neck fovea capitis Posterior Femur lesser trochanter medial epicondyle gluteal tuberosity medial condyle linea aspera Intercondylar fossa greater trochanter lateral condyle lateral epicondyle Tibia medial condyle medial malleolus anterior crest lateral condyle tibial tuberosity Fibula lateral malleolus head Patella Foot Digits (5) Metatarsals (5) Tarsals (7) Talus Calcaneus Hallux (Great Toe) 1 3 Name of the Individual Phalanx Os coxae • or coxal bones or hip bones or pelvic bones • Right + left coxal bones join each other anteriorly + sacrum posteriorly pelvic girdle • Pelvis (= basin) includes pelvic girdle + coccyx Sacrum + Coccyx • Distal parts of axial skeleton • Highly modified vertebrae • 5 sacral vertebrae fused into single bone, sacrum • Coccyx, or tailbone, consist of 3-5 more or less fused vertebrae Pelvic girdle 32 Pelvis • Each coxal bone is formed by fusion of 3 bones during development: Ilium, Ischium, and Pubis • Iliac crest + spine: superior part of ilium • Sciatic notch: post side of ilium, sciatic nerve passes here • Ischial tuberosity: attachment of post thigh muscles • Pubic crest + tubercle: attachment of abdominal muscles • Pubic crest can be felt anteriorly • Pubic symphysis: joint between both coxal bones Coxal bone 36 Acetabulum • Fossa located on surface of each coxal bone • Articulates with femur hip joint • Articular surface is crescent shaped and occupies only the sup + lat aspects of the fossa • Acetabulum means a shallow vinegar cup, a common household item in ancient times Gluteal injections • Large gluteal muscle common site for intramuscular injection • Large sciatic nerve lies deep injection in superolateral region of hip • Landmarks are anterior superior iliac spine + tubercle of iliac crest Gateways to lower limb Summary: Pelvic girdle • Place of attachment for lower limbs • Supports the weight of body • Protects internal organs • Is complete bony ring much more stable than shoulder girdle but less mobility • Protects developing fetus in woman + forms passageway for fetus during delivery Ilium Ischium Differences btw Male and female pelvis Right Femur anterior tibia 42 posterior Femur • Long bone of thigh having • • • • Proximal head Greater + lesser trochanters Shaft w linea aspera posteriorly Distal end w medial + lateral condyles • Head articulates with acetalbulum forming hip joint • Condyles articulate w • tibia forming tibiofemoral joint • Patella forming patellofemoral joint • Both being part of knee joint • Primary ossification in utero Stages• upper ofepiphysis ossification in femur head at 1 y • greater trochanter at 4 y • lesser trochanter at 12 y Patella • Large sesamoid bone located within tendon of quadriceps femoris muscle group • Articulates w patella groove of femur • Holds tendon away from distal end of femur change tendon angle thus increasing forces that can applied on muscle to tibia less muscle contraction is required to move tibia 46 Talus Tibia • medial bone of leg having • Proximal expanded tibial condyles • Shaft w tibial tuberosity anteriorly and sharp • Lateral facing interosseus border • Distal end w medial malleous • Proximally med + lat tibial condyles articulate w • Medial + lateral femoral condyles forming knee joint • Facet below lateral condyle articulates w head of fibula forming superior tibiofibular joint • Distally articulates w • Fibula inferior tibiofibular joint • Talus ankle joint Fibula • lateral bone of leg having • Proximal head • Irregular shaft w sharp medial facing interosseous border • Expanded distal end w lateral malleolus projecting inferiorly • articulates w • tibia superior + inferior tibiofibular joint • Talus ankle joint Surface anatomy showing bones of lower limb 49 Bones of the foot Bones • Phalanges • Metatarsals • Tarsal bones – 7 in 2 rows + 1 bone in between Joints Ligaments Deep transverse metatarsal ligament Bones of the foot 52 How to learn the 7 tarsal names? • Talus • Calcaneus • Navicular • Cuneiforms: medial, intermediate, lateral • Cuboid Mnemonic for distal row is MILC: medial, intermediate, lateral cuneiforms + Cuboid Mnemonic for proximal 3 bones is: No Thanks Cow That is Navicular, Talus, Calcaneus • Bones of foot do not lie flat in single plane • Longitudinal + transverse arches of the foot • Arches are flexible; absorb and transmit forces during standing and walking