* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Psychology
Impression formation wikipedia , lookup
Social loafing wikipedia , lookup
Belongingness wikipedia , lookup
Carolyn Sherif wikipedia , lookup
Self-categorization theory wikipedia , lookup
Social dilemma wikipedia , lookup
False consensus effect wikipedia , lookup
Albert Bandura wikipedia , lookup
Attitude (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Group dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Communication in small groups wikipedia , lookup
Attitude change wikipedia , lookup
Social tuning wikipedia , lookup
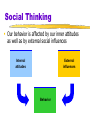
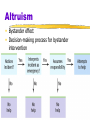
Myers’ EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY (6th Ed) Chapter 15 Social Psychology Modified from: James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers Social Psychology Scientific study of how we think about, influence, & relate to one another Attribution Theory Tendency to give causal explanation for someone’s behavior, often by crediting either situation or person’s disposition Attribution, Attitudes & Actions Fundamental Attribution Error Tendency for observers, when analyzing another’s behavior, to underestimate impact of situation & overestimate impact of personal disposition Attitude Belief & feeling that predisposes one to respond in particular way to objects, people & events Social Thinking Our behavior is affected by our inner attitudes as well as by external social influences Internal attitudes External influences Behavior Social Thinking Attitudes follow behavior Cooperative actions feed mutual liking Actions & Attitudes Foot-in-the-Door Phenomenon Tendency for people who have first agreed to small request to comply later with larger request Role Set of expectations about social position Defines how those in position ought to behave Actions & Attitudes Cognitive Dissonance Theory When attitudes & actions do not coincide, experience tension Act to reduce discomfort (dissonance) we feel when two of thoughts (cognitions) inconsistent Asch’s Conformity Experiments Informational Social Influence Influence resulting from willingness to accept others’ opinions about reality Social Influence Conformity Adjusting one’s behavior or thinking to coincide with group standard Conditions that strengthen (p547) Normative Social Influence Influence resulting from person’s desire to gain approval or avoid disapproval Milgram’s Obedience Experiments Social influences can make people conform to falsehoods or do destructive things Group Influence Social Facilitation Improved performance of tasks in presence of others Occurs with simple or well-learned tasks but not with difficult or not yet mastered tasks Social Loafing Tendency for people in group to exert less effort when pooling efforts toward common goal than when individually accountable Group Influence & Effects Deindividuation Loss of self-awareness & self-restraint in group situations that foster arousal & anonymity Group Polarization Enhancement of group’s prevailing attitudes through discussion within group Groupthink Occurs when desire for harmony in decisionmaking group overrides realistic appraisal of alternatives Social Relations Prejudice Unjustifiable (& usually negative) attitude toward group & members Involves stereotyped beliefs, negative feelings, & predisposition to discriminatory action Aggression Any physical or verbal behavior intended to hurt or destroy Altruism Bystander effect Decision-making process for bystander intervention THE END