* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 5
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
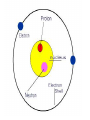
~400 BC DEMOCRITUS VS. ARISTOTLE •Came up with the word atom “atomos” •Said matter was made of atoms •Said matter was uniform throughout, NOT made of atoms •People believed him, even though he was wrong! ~1800 AD JOHN DALTON MODERN ATOMIC THEORY •Atoms can not be created, divided, or destroyed. •Elements have their own unique atoms. •Atoms of elements combine to make new compounds. ~1900 AD JJ THOMSON PLUM PUDDING MODEL •Atom was mostly empty space. •Pudding was positive field and raisins were negative particles (called corpuscles). •Corpuscles made up most of the weight of the atom. ~1909 ERNEST RUTHERFORD DISCOVERED NUCLEUS •Center of atom was called nucleus. •Nucleus made up most of the weight of the atom. •Electrons were negative particles that randomly orbited the nucleus. ~1912 NIELS BOHR ELECTRON ORBITALS •Electrons orbited the nucleus on 7 different energy levels. •Electrons furthest away from the nucleus had the most energy. ~1926 ELECTRON CLOUD MODEL •Designed by a group of scientists. •Electron cloud is 10,000 times larger than the nucleus, but is still mostly empty. •Electrons are in the cloud but can not be pinpointed at an exact time because they move so quickly. DMITRI MENDELEEV---1860 •First periodic table based on atomic mass •Was able to predict where missing elements would be filled in later HENRY MOSELEY---1914 •Rearranged elements according to atomic number •Current table we use today, with elements filled in as they are discovered or created 6 C Carbon 12.0 ISOTOPES of an element have the same number of protons and electrons, but a different number of neutrons. 5 B Boron 10.8 GROUPS (18) P E R I O D S (7) METAL, NON-METAL, OR METALLOID •Also called semi-conductors •Brittle and dull as a solid •Can be dull OR shiny •Ductile •Good conductor of heat and electricity •Left side of periodic table •Malleable •Mostly gases •Mostly solids •Not ductile or malleable •Poor conductor of heat and electricity •Right side of periodic table •Shiny •Stair step of periodic table • Non-metals • Metalloids • Metals • • • • Alkali metals Alkaline earth metals Halogen Hydrogen • Inner transitions • Noble gases • Transition elements Alkali Metals: Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr Alkaline Earth Metals: Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra Ti, Fe, Ni, Cu, Ag, Au, Cd, Hg, U Boron Group: B, Al, Ga, In, Tl Carbon Group: C, Si, Ge, Sn, Pb Nitrogen Group: N, P, As, Sb, Bi Oxygen Group: O, S, Se, Te, Po Halogens: F, Cl, Br, I, At Noble Gases: He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn H