* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download atoms - Wappingers Central School
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
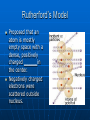
ATOMS THE BUILDING BLOCKS OF MATTER The Greek Model Democritus concluded that matter could not be divided into smaller and smaller pieces forever. • The smallest piece would be obtained and would be . • He named this smallest piece of matter an . • He hypothesized that atoms were _____ and made of the same material. Dalton’s Model All elements are composed of atoms. Atoms of the same element are exactly _____. Atoms of different elements are _______. Compounds are formed by joining of atoms of _________ elements. Thomson’s Model The atom is made of a puddinglike positively charged material throughout which negatively charged (_______) electrons were scattered, like plums in a pudding! Rutherford’s Model Proposed that an atom is mostly empty space with a dense, positively charged ______in the center. Negatively charged electrons were scattered outside nucleus. Bohr Model Electrons move in definite orbits around the nucleus. These orbits, or __________, are located at certain distances from the nucleus. Wave Model Electrons do not move around an atom in a _______ path. Scientists can only predict where an electron may be. Location is based on how much _____ the electron has. Modern Atomic Theory Based on Rutherford’s Model, Bohr’s Model and wave mechanics. • An atom has a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by a large region in which there are enough electrons to make the atom _______.