* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download July 2015 Page 1 of 2 - Mobile County Public Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Bra–ket notation wikipedia , lookup
Musical notation wikipedia , lookup
Abuse of notation wikipedia , lookup
Ethnomathematics wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Big O notation wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical model wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Foundations of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematical notation wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Real number wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
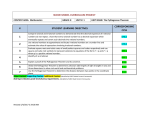
MOBILE COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS DIVISION OF CURRICULUM & INSTRUCTION MIDDLE SCHOOL PACING GUIDE AT A GLANCE FALL SEMESTER 2015-2016 Mathematics 8 Advanced ALCOS Standards/Objectives Text Reference First Quarter Fluency Standards – Add, subtract, multiply, and divide rational numbers. Math 7 Advanced Review Unit 1 Rational, Irrational Numbers, Integer with Exponents Review 1 Know that numbers that are not rational are irrational. Understand informally that every number has a decimal expansion; for rational numbers show that the decimal expansion repeats eventually, and convert a decimal expansion which repeats eventually into a rational number. [8-NS1] 2 Use rational approximations or irrational numbers to compare the size of irrational numbers, locate them approximately on a number line diagram, and estimate the value of expressions. [8-NS2] 3 Know and apply the properties of integer exponents to generate equivalent numerical expressions. [8-EE1] 4 Use square root and cube root symbols to represent solutions to equations of the form x2 = p and x3 = p, where p is a positive rational number. Evaluate square roots of small perfect squares and cube roots of small perfect cubes. Know that √2 is irrational. [8-EE2] Unit 2 Scientific Notations Perform operations with numbers expressed in scientific notation, including problems where both decimal and scientific notation are used. Use scientific notation and choose units of appropriate size for measurements of very large or very small quantities (e.g., use millimeters per year for seafloor spreading). Interpret scientific notation that has been generated by technology. [8-EE4] Chapter 1 Sections: 1.6 – 1.7 Unit 4 Transformations Review Coordinate Plane Verify experimentally the properties of rotations, reflections, and translations: [8-G1] Chapter 6 Sections: 6.1 – 6.3 Lesson: IQL 6-1, 6-1, 6-2, IQL6-3, 6-3, 7-1 a. Lines are taken to lines, and line segments are taken to line segments of the same length. [8-G1a] Lesson: IQL 6-1,7-1 b. Angles are taken to angles of the same measure. [8-G1b]. Lesson: IQL 6-1,7-1 c. Parallel lines are taken to parallel lines. [8-G1c] Lesson: IQL 6-1 July 2015 Chapter 7 Section - 7.1 Page 1 of 2 MOBILE COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS DIVISION OF CURRICULUM & INSTRUCTION MIDDLE SCHOOL PACING GUIDE AT A GLANCE FALL SEMESTER 2015-2016 Mathematics 8 Advanced ALCOS Standards/Objectives Text Reference First Quarter Fluency Standards – Add, subtract, multiply, and divide rational numbers. 19 17 18 Unit 4 (Continued) Transformations Understand that a two-dimensional figure is similar to another if the second can be obtained from the first by a sequence of rotations, reflections, translations, and dilations; given two similar twodimensional figures, describe a sequence that exhibits the similarity between them. [8-G4] Understand that two-dimensional figure is similar to another if the second can be obtained fro m the first by a sequence of rotations, reflections, and translations; given two congruent figures, describe a sequence that exhibits the congruence between them.[8-G2] Describe the effect of dilations, translations, rotations, and reflections on two-dimensional figures using coordinates. [8-G3] Unit 5 Bivariate Statistics Construct and interpret scatter plots for bivariate measurement data to investigate patterns of association between two quantities. Describe patterns such as clustering, outliers, positive or negative association, linear association, and nonlinear association. [8-SP1] Know that straight lines are widely used to model relationships between two quantitative variables. For scatter plots that suggest a linear association, informally assess the model fit by judging the closeness of the data points to the line. [8-SP2] Use the equation of a linear model to solve problems in the context of bivariate measurement data, interpreting the slope and intercept. [8-SP3] Understand that patterns of association can also be seen in bivariate categorical data by displaying frequencies and relative frequencies in a two-way table. Construct and interpret a two-way table summarizing data on two categorical variables collected from the same subjects. Use relative frequencies calculated for rows or columns to describe possible association between the two variables. [8-SP4] Chapter 6 Section - 6.4 Chapter 7 Sections: 7.3 – 7.4 Sections: 7.1 – 7.2 Chapter 6 Sections: 6.1 – 6.4 Chapter 9 Sections: 9.1 – 9.3 End of Quarter 1 District Fluency Test End of Quarter Testing July 2015 Page 2 of 2