* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 5: Heredity
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
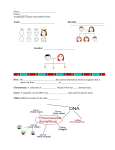
Unit 5: Heredity Genetics physical • Eye color, nose shape, and many other ___________ features are inherited from parents. some of the traits that are ___________ collection of traits, all inherited from its • An organism is a ___________ __________ parents traits from parent to Heredity • ___________-is the passing of ________ offspring Alleles forms of a trait that a _______ gene may • _________different ________ have Genetics chromosomes separates during ________ meiosis • When a pair of ______________ different sex cells alleles for each trait also separate into __________ one allele for each trait sex cell has ______ • Every ______ Offspring inherit one allele for a trait from each parent • ___________ Genetics study of how traits are ___________ inherited • ___________the _______ through the interactions of ________ alleles Genetics pea plants helped scientists understand • Experiments with ______ human traits ________ Gregor Mendel • _________ _______ was an Australian monk who had an interest in ________ plants from an early age Scientific ________ method and • Mendel spent years carefully using the ________ traits pass from one ___________ discovered how ________ generation to the next probability to • Mendel was the first to use the mathematics of ____________ explain __________ heredity Wildcats Share • Before Mendel scientists studying genetics often studied many traits at one time. Mendel was the first to trace one trait through several generations. • Why do you think Mendel was more successful in making discoveries using the scientific method? Genetics trait • Each time Mendel studied a ________, he crossed two plants different expressions of the trait and found that new with _________ plants looked like ______ one of the parents Hybrid different genetic • _________offspring that received __________ information, or ________ alleles from each parent produces the same traits • An organism that always ___________ purebred generation after ____________ generation is called a __________ Genetics Cross-pollination • In Mendel’s experiment he used a process called _____________ tall plants with purebred to pollinate, by hand, purebred ______ ________ short plants seeds that produced _____ tall plants • This pollination resulted in _______ Dominant dominates another • ___________a factor that covers up, or ___________, form of that trait Recessive a trait that is covered up, or dominated, by another • __________trait and seems to __________ form of that _______ disappear Wildcats Share • Refer back to the activity traits activity we worked on in class. Looking at the percentages calculated, predict if the following traits are dominant or recessive. Prediction Answer • Trait Dimples Rolling tongue Dominant Dominant Thumbs crossed right over left Recessive Earlobes attached Recessive Cleft Chin Dominant Genetics Probability is a branch or mathematics that helps you • ____________ predict the chance that something will _________ happen _________ coin lands on the side you • If you flip a coin the probability the ______ want is ___ 1 out of ____ 2 predictions accurate was that • One thing that made Mendel’s ____________ he worked with _______ large numbers of plants 8 years 30,000 pea plants over ___ • Mendel studied almost ________ increased Mendel’s chances of seeing ____________ repeatable • This ___________ patterns Genetics Punnett_______square a tool to predict the ____________ probability of a • ________ different ways alleles can certain trait in offspring that shows __________ combine dominant alleles, and lowercase • Uppercase letters represent __________ __________ recessive genetic makeup of an organism Genotype • ____________________ appearance and behavior of Phenotype outward physical ____________ • ___________an organism as a result of its ___________ genotype Genetics two alleles for every trait • Most cells in your body have _____ Homozygous an organism with ______ two alleles that are the • __________________ same • Example: TT for tall plant, tt for short plant Heterozygous • ______________an organism that has two _________ different alleles for a trait • Example: Tt hybrid plants Mendel created Genetics Punnett square • When creating a _________ ________ the two alleles from one top parent are written along the _______, one letter per square, and the two alleles from the other parent are written on the ______ side allele donated by • Each square of the grid is filled in with one _______ parent each ________ squares • The letters that you use to fill in each of the __________ genotypes of possible offspring that the parents represent the ___________ could produce Genetics • Mendel developed the following principles through his research DNA genes, or even though he didn’t know anything about _______, ______________ chromosomes alleles on chromosomes controlled by ________ 1. Traits are ___________ dominant or ___________ recessive 2. An allele’s effect is ___________ chromosomes separates during _________ meiosis 3. When a pair of ______________ separate sex cells the different alleles for a trait move into __________ Genetics Since Mendel • Mendel’s work was later re-tested and is was discovered that not alleles of all organisms display ___________ complete dominance all ________ and recession red flowers with • One scientist found when he crossed ______ white flowers he got _______ pink flowers _______ Incomplete dominance • ____________ ___________- production of a phenotype that is intermediate between the two _____________ _____________ homozygous parents Genetics Since Mendel • Mendel didn’t discover incomplete dominance because he two alleles studied traits that were controlled by ______ multiple alleles if there are more than • A trait is controlled by __________ two alleles that control the trait. ______ three • Traits controlled by multiple alleles result in more than _______ phenotypes of that trait. multiple alleles • _______ Blood type in humans is an example of __________ four phenotypes that produce _______ Genetics Since Mendel A B and ____. O • The allele for blood type are called _____, ____, A and ____ O is recessive to _____ B Where ____ B allele, both A allele and one ____ • When a person inherits one ____ AB are expressed and the phenotype is ______ phenotype A has a genotype of _____ AA or _____ AO • A person with ___________ phenotype B has a genotype of _____ BO BB or _____ • A person with ___________ O has a genotype of ______ OO • A person with phenotype ____ Genetics Since Mendel Polygenic inheritance group of gene pairs • _________ __________- occurs when a _______ acts together to produce a trait • Ex: Height and the color of your eyes, skin, and hair alleles produce a wide variety of • The effects of many _______ ____________ phenotypes Environment • _______________ also plays an important role in the ___________ expression of these traits • Other traits controlled by phylogenic inheritance are: Grain color in wheat and milk and egg production in cows and chickens Genetics Since Mendel Genetic disorders recessive • Many human _________ ________ are caused by __________ genes • Such genetic disorders occur when both parents have a recessive allele responsive for the __________ ______ disorder heterozygous they don’t show any • Because the parents are ______________ __________ symptoms of the disorder offspring inherits two recessive alleles it will be • If the __________ homozygous and have symptoms of the genetic disorder _____________ Genetics Since Mendel • What determines the sex of an individual? Fruit flies • Scientist studied this question using ______ _____ one pair of ______________ chromosomes that determine • They identified ______ the sex of organisms XX is labeled female and a _____ XY male • A pair of ______ egg produced by a female normally contains one ____ X • Each ______ chromosome X or ____ Y • Males produce sperm that normally have either an ____ chromosome Genetics Since Mendel inherited conditions are linked with the ____ X and ____ Y • Some __________ chromosomes Sex-linked gene_____- an allele inherited on a ______ sex • ______________ chromosome • Ex: Color blindness • More common in males that females because males only have one X chromosome, which this condition is associated with, females have two X chromosomes, which means both must carry the allele for a female to be color blind Wildcats share • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BD6h-wDj7bw • While watching the video find answers to the following questions, we will have a discussion after the video 1. Why must one X chromosome be inactivated in females? 2. What are differences between the active and inactive X chromosomes? 3. Does the same X chromosome always win? 4. What give calico cats their different colors? Genetics Since Mendel pedigree is a visual tool for following a _______ trait • A __________ through generations of a family completely filled shape shows that a trait is ______ seen in that • A ____________ person Half-colored • ______________ shaped indicate carriers Empty shapes represent organisms that do not have a ______ trait • ________ carriers and are not __________ Genetics Since Mendel geneticists • Pedigrees are useful tools for _____________ recessive • Geneticists can determine if a trait is ___________, dominant, Sex-linked ____________, or has come other pattern of inheritance probability a baby will have specific • They can also predict the ____________ trait Pedigrees are also important in __________ breeding plants or • ___________ animals Genetics Since Mendel yield and nutritional content of • Pedigrees are used to increase ________ ___________ livestock and plant crops • Also used by __________ breeders of show animals, like dogs, to breed for possible desirable ____________ traits physical health • Issues concerning __________ are also considered when _____________ researching pedigrees Advances in Genetics gene has become a _____________ common • The term _______ word in our society hereditary change the • The principles of _____________ are being used to ________ world Genetic engineering • _________ __________- scientists experimenting with biological and chemical methods to change the ___________ arrangement ______________ of a gene’s DNA to improve _______ crop production, produce large volumes of __________, medicine and change how cells perform their normal functions. Advances in Genetics genetic recombinant DNA is one method of _________ • Making _____________ engineering DNA is made by __________ inserting a useful segment of DNA • This _______ from one ___________ organism into a ___________ bacterium insulin to treat Type I • This method can be used to make ________ diabetes, and chemical to treat __________ and other diseases cancer Advances in Genetics Gene therapy • _______ _________ is another kind of genetic engineering virus normal allele being placed in a _______ • This process involved a _________ allele when it infects its _________ target • The virus then delivers the ________ cell defective one normal • The __________ allele then replaces the __________ Cystic fibrosis • Research is being done using this method to treat _______ ________, some kinds of _________, and other __________ genetic disorders cancer Advances in Genetics selective breeding • For thousands of years people have used __________ food and clothing to improve the plants they use for _______ Genetic engineering • _________ __________ along with selective breeding are being used to make ______________ improvements to food desired trait can now be • Genes from a plant that produce a _________ different plant inserted into a __________ research • Developments are still being made in this field and __________ impacts is still being done to determine the __________