* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Immunisation update
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Tuberculosis wikipedia , lookup
Bioterrorism wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Yellow fever wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Poliomyelitis eradication wikipedia , lookup
Poliomyelitis wikipedia , lookup
Meningococcal disease wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Yellow fever in Buenos Aires wikipedia , lookup
Typhoid fever wikipedia , lookup
Cysticercosis wikipedia , lookup
Anthrax vaccine adsorbed wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
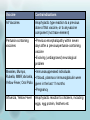
Immunisation Update Changes to the immunisation schedule Contraindications and precautions to vaccination Epidemic update Three significant changes to the immunisation schedule in 2008: – New pneumococcal vaccine for infants – MeNZB vaccine programme – HPV vaccine programme New pneumococcal vaccine for infants PCV7 (Prevenar®) vaccine has been added Effective in children < 2 years Previous vaccine 23PPV (Pneumovax23) not effective in infants Given at 6 weeks, 5 and 15 months Children at high risk still have PCV7 + 23PPV MeNZB vaccine programme in cases group B meningococcus MeNZB now removed from National immunisation schedule Contraindications and precautions to vaccination Vaccine Contraindications All Vaccines Anaphylactic type reaction to a previous dose of that vaccine, or to anyvaccine component (not trace element) Pertussis-containing vaccines •Previous encephalopathy within seven days after a previouspertussis-containing vaccine •Evolving (undiagnosed) neurological problem Measles, Mumps, •Immunosuppressed individuals Rubella, MMR,Varicella, •If blood, plasma or immunoglobulin were Yellow Fever, Oral Polio given in the last 11 months •Pregnancy Influenza, Yellow Fever Anaphylactic reaction to chickens, including eggs, egg protein, feathers etc Precautions There are a number of precautions to vaccination: Giving a live vaccine less than four weeks after another live vaccine Pregnancy . Allergy to Vaccine components History of Guillain Barré Syndrome Thrombocytopenia or history of thrombocytopenic purpura and MMR Haemophilia and related bleeding disorders False contraindications The following conditions or circumstances are not contraindications to vaccination: Minor infections without significant fever or systemic upset Asthma, hayfever, eczema, “snuffles” Food or medications allergy Treatment with antibiotics or locally acting steroids Pregnancy in the child’s mother A child who is breastfeeding Neonatal jaundice Low weight in an otherwise healthy child (continued on next slide) False contraindications (..contd) The child being over the usual age for immunisation Family history of vaccine reactions, seizures or Sudden Infant Death Syndrome Prematurity in an otherwise well infant who is not in hospital Established neurological conditions such as cerebral palsy or Down syndrome Contact with an infectious disease Clinical history of pertussis, measles, mumps or rubella (clinical history without laboratory confirmation can not be taken as proof of immunity) Epidemic update Pertussis Measles Pertussis New Zealand has a pertussis epidemic every four to five years – currently in early phases Infants are vulnerable to disease The best way to contain an epidemic is immunisation and effective management of confirmed cases Exclude confirmed cases from school or work Pertussis is a notifiable disease to MOH Measles in cases since start of 2009 95% of popn must be immunised to avoid outbreaks Difficult as efficacy of measles vaccine is 90-95% All children should be vaccined at 15 months and 4 years