* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Marketing Mix - EMS Secondary Department
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Revenue management wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Planned obsolescence wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Supermarket wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Product placement wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Predictive engineering analytics wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Pricing science wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Price discrimination wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
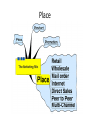
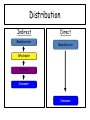
What is the marketing mix? The Marketing Mix • Lesson Outcomes: • • • • Identify and explain the elements of the marketing mix Demonstrate an understanding of the product life cycle Understand how pricing decisions are made Understand the significance of price elasticity of demand • Appreciate the importance of distribution channels and the factors that determine the selection of them • Understand the role of promotion The Marketing mix • The marketing mix is all the key activities that are involved in the marketing (selling) of a business’ products/services. • This is referred to as the four Ps: Product, Price, Place, Promotion • The mix will vary depending on the life of a product The Marketing Mix, known as the 4Ps The Marketing Mix • This provides an excellent framework for developing marketing plans. • People in the marketing department of a company need to make many decisions before launching a product. What are you going to sell? You need to consider the details of the goods or services being sold Where and how can the customers obtain the product or service? How much are you going to charge? What pricing strategies might you use? How will you ensure that the customers know about the product or service? Objectives of developing the marketing mix 1. To support brand building 2. To satisfy the needs and aspirations of targeting group of customers Product • The term Product includes: – – – – – – – – Quality Packaging Appearance Brand Guarantee/warranty After-sales service Variations and product range Functionality • Including features Quality, cool, product Product Development Stages 1. Generate ideas 2. Further research of best ideas 3. Decide if the company will be able to sell enough 4. Develop prototype 5. Test launch 6. Full launch Product Life Cycle 1. Research and development • This is when the company is creating new products, and testing them to see if people like them • The costs are high, and they have no money coming in 2 - Introduction • Introduction – the product is new, no one knows about it – The company is spending lots of money on advertising and to secure distribution • They are probably still losing money 3 - Growth • Shops are stocking the product, and the advertising has helped the product to become better known – The company is starting to make money 4 - Maturity • Maturity – the product is well known, and sales are high – The company is making money 5 - Decline • Decline – people are starting to lose interest in the product, and sales are decreasing – If sales go down too much, they may have to withdraw the product Extension strategies • The maturity stage is a good stage for the company in terms of generating cash – The costs of developing the product and establishing it in the market are paid and maturity tends to be the most profitable stage • The longer the company can extend this stage the better it will be for them • This can be done using extension strategies – These are techniques to try to delay the decline stage of the product life cycle Examples of extension strategies • • • • • New flavours/formats Limited editions New packaging Promotions Discounts Can you name three products that have had any of the 4P’s changed to extend there life. ~Activity~ How can the life of the following products be extended? • Nintendo Wii • Kit Kat chocolate bar • Perfume • A waste paper bin Place • This refers to how the product gets to the consumer: – – – – Where it is made Distribution/transportation Warehousing Market coverage (where it is sold) Place Place includes… • Where it’s sold, for example: – Supermarkets – Newsagents – Vending machines – Internet – Mail order • Where it’s made • How it gets there (and how it’s stored) Place • Why is place important in marketing? • 1. 2. 3. 4. There are 4 main methods of distribution – Producer Consumer Producer Retailer Consumer Producer Wholesaler Retailer Consumer Producer Agent Wholesaler Retailer Consumer Distribution Indirect Manufacturer Direct Manufacturer Wholesaler Retailer Consumer Consumer ~Activity~ Which method of distribution would you use for the following businesses? Give reasons for your choice. 1. A business making quality jeans 2. A small business making hand made pottery in a craft centre 3. A farmer selling milk 4. A business selling holidays Place - E-commerce • Marketing which brings the buyer and seller together over the internet • E-commerce is becoming more and more important as more and more people use the internet. 8-10% of total retail sales in the UK is online. • All businesses need to include e-commerce in their marketing strategies There is the opportunity to sell products to a larger market and therefore make more profit Why do businesses feel they must use e-commerce? If their competitors are using ecommerce, they might lose customers if they do not They can become more productive (produce more with fewer workers) and can save wage costs Online sales now 8-10% of Total retail sales in UK How can you transport goods from A-B? • • • • • • Road Haulage Railways Canal and river Sea Freight Air Freight Pipelines • Which method is cheapest? • Which method is fastest? • Which method is more expensive? Expensive product? Sold to producer or consumer? Purchased often? Factors affecting channels of distribution Technical product? Where competitors goods are sold? Perishable product? Selling abroad? Location of customers? Complete Exam question 2 (a-e), pg 197 Price starter • Unlike most globes, these Magic Globes actually revolve constantly (completing a full revolution every 18 seconds) without any selfspinning required. Just pop in a battery and watch it go! • Designed by the Italian design guru Raffaele Iannello, the 'Voodoo' knife block, is destined to find its place among the greats in the top design museums of the world • How much would you pay for this? • How much would you pay for this? Price starter • £24.99 • £59.99 Price • The process of setting a monetary value for a good/service. • A business can adopt pricing strategies for several reasons: • To try to break into a new market • To try to increase its market share • To try to increase its profits • To make sure all its cost are covered and a particular profit is earned So, what are pricing strategies? Pricing Strategies Penetration Pricing Launch your product at a low price, gain market share, and then raise your price Dynamic Pricing Different people are charged different amounts for the same thing e.g. train tickets Skimming charge a very high price when the product is first launched so “rich early adopters” buy the product e.g. iPhone Psychological Pricing When companies charge, for example, £9.99 so they can say “less than £10” Promotional Pricing When a product is sold at a very low price for a short time. For example, buy one get one free, 20% extra free etc. Cost Plus Pricing Estimating how much will be produced, adding up the costs of production and the adding a percentage mark up for profit Competitive Pricing Setting a price in line with or just below your competitors ~Activity~ Study the following situations and name the pricing strategy that is being described: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. A new hardback is published at £20. Two months later it is sold as a paper back for £10. Skimming A Hairdressers in Al Rayyan offers haircuts to OAPs at half price every other day. Dynamic Pricing A bicycle manufacture introduces a new model at a low price in order to attract sales. Penetration Pricing Competitor Pricing A chemist shop in Al Saad researches the price of particular brands of toothpaste in all the local outlets and then charges the same price. A florist in The Pearl sets her prices to cover her total costs plus a little profit. Cost Plus Elasticity of demand • Elasticity of demand is a measure of how much the quantity demanded of a product responds to a change in price. • Elasticity of demand can be shown in the following % change in quantity demanded formula: • Elasticity of demand= %change in price • Elastic demand is represented by figures which are higher than 1. • Inelastic demand is represented by figures of less than -1. Elastic demand • If quantity demanded is very responsive to price changes, then a small change in price will lead to relatively large change in quantity demanded. • In this case we say that demand is ELASTIC! • For example, if the price of a standard washing powder rose by two or three pence, then customers could easily switch to a cheaper substitute. Inelastic demand • Where quantity demanded is relatively unresponsive to price change, demand is inelastic. • An example of this is Petrol. Even though the price is relatively high, people are prepared to buy Petrol to fuel their cars. Activity 1. • • • • • Which of the goods listed below are likely to have the most elastic demand resulting from a rise in price? Explain your answers. The iPhone Swan Vetas matches The Daily Mail newspaper A container of Saxo table salt A packet of cereal Activity 13.3 pg 173 Promotion • Promotion gives the consumer information about the rest of the marketing mix. • It is how you create awareness of your brand. • Promotion does not necessarily lead to increase profits. What is a brand? Companies with strong brands • Can charge customers higher prices • Can persuade shops to stock their products • Are more likely to get people ‘trying’ their products for the first time • Have customer loyalty (so they will repeat purchase) • Have customer trust • Enable companies to enter new markets (e.g. Sony) Every companies build brands by consistently getting the four Ps right If the product is great, the price is fair, the promotion is attentiongrabbing and it’s sold in the right places… the whole brand benefits Also, by launching/promoting a new product, they are also promoting the whole brand What are the different methods of advertising? (Think of the different media) Advertising • Advertising is when the brand owner pays to display messages about their brand, and includes the following media: – – – – – – – – – – – Television Cinema Posters Transport (e.g. bus sides) Radio Newspapers/magazines Internet Text messages Direct mail Leaflets Etc. Each has it advantages and disadvantages Advertising – Letting customers know about your product or service Can be informative or persuasive TV Advertising VW are trying to make the Golf a generic brand A generic brand is a brand that defines a whole market. Sometimes people don’t even know that it is not actually the real name e.g. Hoover, Cellotape Can you think of any other generic brands? Radio advertising Sponsorship • When a company sponsors a thing, team or an individual • The company (sponsor) hopes to gain a positive image from the thing/team/person/ event they sponsor Sales promotion • These are tactics used by firms to increase sales: – Price reductions – Free gifts – Point of sale – Competitions – Free samples – BOGOF – After-sale service Definitions • Point of sale – this is when you advertise a product where it is sold – For example, posters advertising new films in Blockbusters Definitions • After-sale service – this is when companies still have contact with customers even after they have bought the product – For example, if you buy a car and it goes wrong, an example of good after-sales service would be that company providing a courtesy car What are the advantages of sales promotion? Public relations • Companies try to influence what the journalists write/say • They want newspapers, television programs, magazines, radio stations etc. to say good things about their products - Press releases PR Events Freebies Increasingly environmental policies in aims and objectives ~Activity~ In pairs decide which promotional method would you use for the following products and explain your answer. – A new flavoured chocolate bar – A new pair of NIKE trainers – A new Dell computer – A sun holiday – A restaurant – A new movie in the cinema Marketing mix decision rely heavily on the budget allocated to the marketing department. What is a budget? How has technology influenced promotion? Complete Exam question 1 (a-d), pg 189