* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download information technology entrepreneurshp
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Strategic management wikipedia , lookup
Business process wikipedia , lookup
Channel coordination wikipedia , lookup
Value proposition wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Market environment wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Marketing ethics wikipedia , lookup
Services marketing wikipedia , lookup
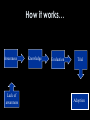
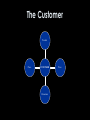
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY ENTREPRENEURSHP CLASS 10: BUILDING & DEVELOPING A BRAND Elikem Nutifafa Kuenyhia Management Consultant & Corporate Lawyer Agenda for class 11 • The 4 Ps. • The importance of the customer. • Tactics to maximise benefits of marketing strategies. • Draw up a marketing strategy for a company. What is Marketing? • Management process which identifies, anticipates and supplies customer requirements efficiently and profitably [CIM (UK)] • Marketing is a human activity directed at satisfying needs and wants through exchange processes [Kotler] • The process of winning and retaining customers [Kuenyehia] Characteristics of modern marketing • It is operational • It is customer oriented • It emphasises mutuality of benefit • It is value driven Customer!! Customer!! Customer!! Conduct customer research to understand what the needs, wants and desires of customers are. Customers expect and demand more, because they know they can get more. They do not need to deal with companies that don’t understand and appreciate this. Elements of marketing strategy The 4 Ps • Product • Price • Place • Promotion How it works… Awareness Lack of awareness Knowledge Evaluation Trial Adoption The Customer Product Place CUSTOMER Promotion Price Product • Physical products • Experience of the service • Image and emotional connotations associated with the product or service • Entire spectrum of delivering and consuming the product or service Approaches to product ideation • Reactive approach • Proactive approach Price • Will the customer be willing to pay the price you are asking for? • How much is the value of your product worth to the customer? • What pain of the customer does your product or service seek to address? Pricing strategies • Penetration – Going with a low prices to beat the competition – Involves initial high investments • Skimming – Low entry barriers – Not so tough competition Pricing tactics • Price flexibility • Level pricing • Introductory pricing • Discounts • Allowances • Geographic terms Place It refers to the place or method of distribution. Place Location!! Location!! Location!! Location!!! Place – Choice of distribution channel • How many potential customers will you have? • Will they be companies or individuals? • Does the product require explanation? • Is it an upper or lower end price product? Examples of distribution channels • Third party retailers • Agents • Franchising • Wholesalers • Stores • Own sales staff • Internet Promotion Potential customers must first HEAR about your product or service and be CONVINCED to purchase. Promotion - Components • Advertising Communication to potential customers through the mass media with the view to; 1.Attract attention 2.Inform 3.Persuade 4.Inspire confidence in the product Promotion - Components cont. • Personal selling Involves the art of persuasive sales on a one-to-one basis Promotion cont. Effective communication must: – Explain the value of your product or service to potential customers – Convince them that your product or service meets their needs better than competing or alternative solutions. Promotion - Tactics How to get the customer’s attention: – Classic advertising i.e. newspapers, magazines, trade magazines, radio, TV, etc. – Public relations – Exhibitions, trade fairs – Customer visits – Mass selling – Copywriting Promotion cont. - Focus Focus on the people who make the purchasing decisions; E.g. when marketing kids’ toys, the focus should be on the parents especially mothers. Conclusion There are internal and external variables which can not be controlled, no matter the amount of work gone into a strategy. Forget about the external factors and concentrate on the internal factors like budget, personnel, creativity, etc. in order to build a solid brand.