* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 4 - Immunology and Public Health
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
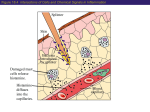
Unit 4 Immunology and Public Health Unit 4 – Immunology and Public Health 1. The Immune System a)Non-specific defences b)Specific cellular defences 2. Infectious Diseases and immunity a)Transmission and control b)Active Immunisation and Vaccination and the evasion of immune responses Can you now …. • Name some of the body’s physical and chemical defence barriers • Explain the role of epithelial cells in defence • state when an inflammatory response might occur • describe the steps and cells involved in the inflammatory response • describe the role and process of phagocytosis • describe the action of natural killer (NK) cells Quick Question Complete the sentences below using the letters or words in the box below: A. Pathogen B. Skin C. Airways D. Non-specific E. Specific F. Epithelial 1. A microbe that could cause us harm is known as a A or Pathogen _________ B or Skin F or Epithelial 2. The ___________cells that line our ______ and C or airways ____________act as a physical barrier to pathogens. D or non-specific 3. This is an example of _____________defence. Quick Question Match the immune factor to it’s function 1. Cytokine A. Triggers the inflammatory response. 2. Complement antimicrobial proteins B. Attract phagocytes 3. Phagocyte C. Amplifies the immune response. 4. Mast Cell D. Engulfs pathogens. Quick Question Events in the inflammatory response are described below. 1 Clotting elements coagulate the blood 2 Phagocytes engulf pathogens 3 Blood capillaries dilate and increase in permeability 4 Healing 5 Mast cell releases cytokines and histamine The sequence in which these events occur following is A 2, 3, 1, 5, 4 B 2, 1, 3, 4, 5 C 5, 3, 2, 1, 4 D 5, 2, 1, 3, 4. Questions • Decide whether each of the following statements is true or false. If it is false, correct the word in bold to make it true. COPY THE CORRECT SENTENCES IN YOUR JOTTER 1. The process of programmed cell death of a pathogen infected cell is called phagocytosis 2. If white blood cells detect tissue damage, they release cytokines which attract other white blood cells to the site of injury 3. A phagocytes cytoplasm contains ribosomes full of digestive enzymes 4. Following injury, mast cells in connective tissue release histamine which causes vasodilation 5. Decreased capillary permeability occurs at an infected site showing inflammation. F T F T F Quick Question 1. Which white blood cell secretes histamine? A. Phagocytes B. Mast cells C. Complement D. Natural killer cells Quick Question 2. Which of the following is NOT an affect brought on by histamine at the site of an infection? A. Vasodilation B. Clotting of blood C. Attraction of phagocytes to site of infection D. Increased capillary permeability Trick!! There are only 2 effects of histamine presence Quick Question 3. Cytokines are secreted at the site of infection. What effect does this have? Antimicrobial protein / clotting element is drawn to the site of infection of the skin (cut) Quick Question 4. Which of the following describes the action of phagocytes? A. Stimulates inflammatory response B. releases histamine C. Causes programmed cell death D. Engulfs pathogenic cell Quick Question 5. Describe the action of Natural Killer cells Causes cell to self destruct Extended Answer Question • Describe non-specific defences that the body uses to protect itself from pathogens. (8 marks) Higher Human Biology Revised 2013 1. The skin prevents the entry of pathogens / is a physical barrier. 2. Epithelial cells (in cavity linings) produce (protective chemical) secretions 3. Description of one non-specific defence e.g. mucus in windpipe / acid in stomach / lysozyme or anti-bacterial substances in tears / coughing or sneezing / blood clotting 4. The inflammatory response is caused by the release of histamine from mast cells 5. Vasodilation / increased capillary permeability / increased blood flow (occurs) 6. Increased blood flow / secretion of cytokines results in the accumulation of phagocytes 7. It also results in the delivery of antimicrobial proteins / clotting elements to the site 8. Phagocytes recognise surface antigens or protein markers on pathogens 9. They then destroy the pathogen by engulfing it / by phagocytosis 10. Natural killer (NK) cells induce the pathogen to destroy itself / apoptosis 11. (The NK cells cause) the pathogen to produce digestive / self-destructive enzymes 12. Phagocytes / NK cells release cytokines that stimulates the (specific) immune response 8 marks