* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Angiogenesis
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
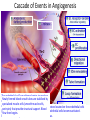
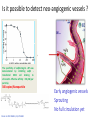
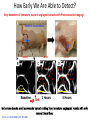
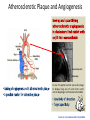
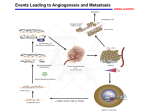
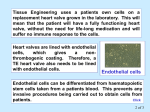
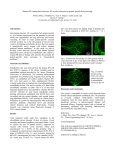
Module 1-b Angiogenesis Angiogenesis In order for a tumor to grow beyond 2 mm^3, it must have a steady supply of amino acids, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, oxygen, and growth factors for metastasis and continued growth. Tumors must stimulate angiogenesis, the growth of new blood vessels from preexisting ones so as to obtain these nutrients. Cascade of Events in Angiogenesis The endothelial cell's machinery begins to produce Newly formed blood tubes are stabilized by The Matrix endothelial metalloproteinases cells vessel begin (MMP) to divide are produced new molecules including enzymes. These enzymes Specialized Sprouting endothelial molecules called cells roll adhesion up to form a Individual blood vessel tubes connect to cells, form specialized muscle cells (smooth muscle (proliferate) to dissolve the and tissue migrate in front out through of the sprouting the dissolve tiny holes in the sheath-like covering molecules blood vessel called tube. integrins (avb3, avb5) The angiogenic growth factors bind toserve specific located on the endothelial cells blood vessel loops that can circulate blood. pericytes) that provide structural support. Blood receptors Diseased or injured tissues produce and release growth dissolved vessel tip holes in order of to the accommodate existing vessel it. towards (basement membrane) surrounding all existing growth factors bind to their receptors, the endothelial cells angiogenic become activated. asOnce grappling hooks to help pull thenearby sprouting (EC) of preexisting blood vessels flow then begins. the diseased tissue (tumor). blood vessels. Signals arevessel sent from the cell's surface the nucleus. factors (proteins) thattodiffuse into the nearby tissues new blood sprout forward. Angiogenic Switch Angiogenic Switch Balance is important in every aspect of life ! Antiangiogenesis Targets for Therapy and Imaging • Neovasculature • Proteases that breakdown the ECM (e.g. MMPs) • Growth factors that stimulate endothelial cell proliferation (e.g. VEGF, PDGF, bFGF, IL-8) • Integrins that allow adhesion of endothelial cells (e.g. avb3) • Endothelial cell apoptosis (e.g. TNF…) • Pre-existing Vasculature • Various Vasculature Targeting Agents Timeline of Anti-angiogenic Therapy • 1971: The field began in early 1970s with Judah Folkman’s hypothesis that tumor growth would be halted if it were deprived of a blood supply • 1989: Dr. Napolene Ferra identified and isolate VEGF • 1996: Dr. Jeffery Isner published first clinical trials regarding VEGF • 2004: FDA approves first antiangiogenic drug to treat colorectal cancer (Avastin) Is it possible to detect neo-angiogenic vessels ? The specificity of αvβ3-integrin –NP was demonstrated by inhibiting αvβ3 transfected K293 cell binding to vitronectin. Effective affinity = 50 pM (per particle). Integrin avb3-Targeted 300 copies/Nanoparticle Gold NanoBeacons (GNB) Pan et al. 2010 FASEB J, 25, 875-882 Early angiogenic vessels Sprouting No full circulation yet How Early We Are Able to Detect? Early detection of immature, nascent angiogenic vessels with Photoacoustics Imaging! MATRIGEL MOUSE MODEL 720 nm 720 nm 14 days avb3-GNB Pan et al. 2010 FASEB J, 25, 875-882 720 nm Atherosclerotic Plaque and Angiogenesis In vivo T1 sagittal section spin-echo image to display long axis of aorta from aortic arch to diaphragm of cholesterol-fed rabbit Pan D. et al. Circulation 2010, 122, A20216