* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 18 - King William County Public Schools
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
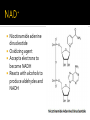
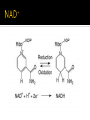
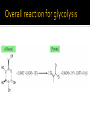
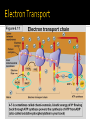
DE Chemistry – King William High School Chemical reactions and substances that provide energy for cell growth 2 types: 1. catabolic reaction – complex molecules are broken down and release energy 2. anabolic reaction – use energy to build large molecules from smaller molecules Stage 1: Digestion polysaccharides monosaccharides fats glycerol & fatty acids proteins amino acids **products go into bloodstream for transport to cells Stage 2: digestion product 2 & 3 carbon cmpds **pyruvate & acetyl-CoA Stage 3: *acetyl-CoA is oxidized in the citric acid cycle *production of energy in mitochondria * products of citric acid cycle (NADH & FADH2) are transferred to electron transport to make ATP (as long as there is enough oxygen in the cells) ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) is released as energy from the oxidation of food ADP + H2O AMP + Pi + 34 kJ Catabolic reactions are energy producing ADP + Pi + 34 kJ ATP + H2O Anabolic reactions are energy requiring (stored ATP hydrolyzes to produce energy) Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide Oxidizing agent Accepts electrons to become NADH Reacts with alcohols to produce aldehydes and NADH Flavin adenine dinucleotide Contains ADP Used in the citric acid cycle Prepares small acyl groups for reactions with enzymes Anaerobic (no oxygen involved) Glucose 2 pyruvate Occurs in cytoplasm Nets 2 ATP & 2 NADH Aerobic conditions – pyruvate is converted to acetyl-coenzyme A Anaerobic conditions – pyruvate is converted to lactate 2 carbon dioxides 3 NADH & 3H+ 1 FADH2 1 GTP (1 ATP) 1 CoA Proton pump – H+ (protons) concentration goes up, pH goes down…makes an electrochemical gradient Protons must move through ATP synthase in order to get back into the matrix When protons move through ATP synthase…energy is generated (ADP ATP) Produces lots of energy Occurs in the mitochondria Produces acetyl-CoA # of Cs determines how much energy is produced About 10% of our energy